Page 176 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 176
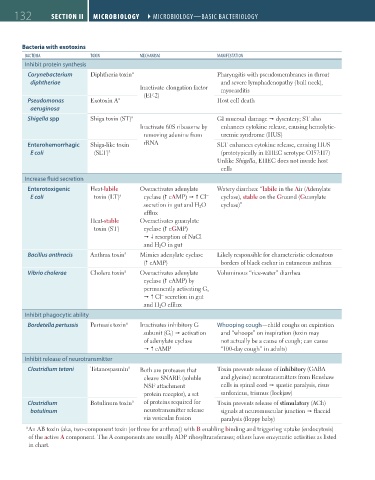
132 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—basic bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—basic bacteriology
Bacteria with exotoxins
bacteria toXiN mecHaNism maNiFestatioN
Inhibit protein synthesis
Corynebacterium Diphtheria toxin a Pharyngitis with pseudomembranes in throat
diphtheriae and severe lymphadenopathy (bull neck),
Inactivate elongation factor myocarditis
(EF-2)
Pseudomonas Exotoxin A a Host cell death
aeruginosa
Shigella spp Shiga toxin (ST) a GI mucosal damage dysentery; ST also
Inactivate 60S ribosome by enhances cytokine release, causing hemolytic-
removing adenine from uremic syndrome (HUS)
Enterohemorrhagic Shiga-like toxin rRNA SLT enhances cytokine release, causing HUS
E coli (SLT) a (prototypically in EHEC serotype O157:H7)
Unlike Shigella, EHEC does not invade host
cells
Increase fluid secretion
Enterotoxigenic Heat-labile Overactivates adenylate Watery diarrhea: “labile in the Air (Adenylate
−
E coli toxin (LT) a cyclase ( cAMP) Cl cyclase), stable on the Ground (Guanylate
secretion in gut and H 2 O cyclase)”
efflux
Heat-stable Overactivates guanylate
toxin (ST) cyclase ( cGMP)
resorption of NaCl
and H 2 O in gut
Bacillus anthracis Anthrax toxin a Mimics adenylate cyclase Likely responsible for characteristic edematous
( cAMP) borders of black eschar in cutaneous anthrax
Vibrio cholerae Cholera toxin a Overactivates adenylate Voluminous “rice-water” diarrhea
cyclase ( cAMP) by
permanently activating G s
−
Cl secretion in gut
and H 2 O efflux
Inhibit phagocytic ability
Bordetella pertussis Pertussis toxin a Inactivates inhibitory G Whooping cough—child coughs on expiration
subunit (G i ) activation and “whoops” on inspiration (toxin may
of adenylate cyclase not actually be a cause of cough; can cause
cAMP “100-day cough” in adults)
Inhibit release of neurotransmitter
Clostridium tetani Tetanospasmin a Both are proteases that Toxin prevents release of inhibitory (GABA
cleave SNARE (soluble and glycine) neurotransmitters from Renshaw
NSF attachment cells in spinal cord spastic paralysis, risus
protein receptor), a set sardonicus, trismus (lockjaw)
Clostridium Botulinum toxin a of proteins required for Toxin prevents release of stimulatory (ACh)
botulinum neurotransmitter release signals at neuromuscular junction flaccid
via vesicular fusion paralysis (floppy baby)
a An AB toxin (aka, two-component toxin [or three for anthrax]) with B enabling binding and triggering uptake (endocytosis)
of the active A component. The A components are usually ADP ribosyltransferases; others have enzymatic activities as listed
in chart.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 132 11/14/19 12:20 PM