Page 180 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 180
136 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology
Staphylococcus Gram ⊕, catalase ⊕, coagulase ⊝, urease ⊕ cocci in clusters. Novobiocin resistant.
saprophyticus Normal flora of female genital tract and perineum.
Second most common cause of uncomplicated UTI in young women (most common is E coli).
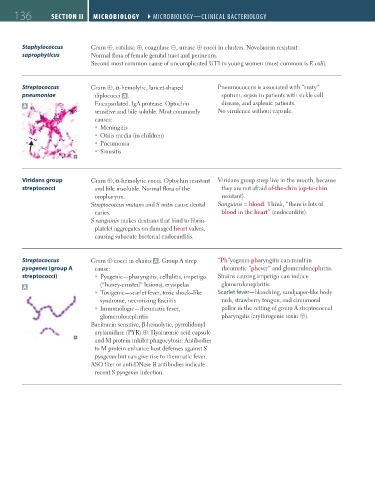
Streptococcus Gram ⊕, α-hemolytic, lancet-shaped Pneumococcus is associated with “rusty”
pneumoniae diplococci A . sputum, sepsis in patients with sickle cell
A Encapsulated. IgA protease. Optochin disease, and asplenic patients.
sensitive and bile soluble. Most commonly No virulence without capsule.
causes:
Meningitis
Otitis media (in children)
Pneumonia
Sinusitis
Viridans group Gram ⊕, α-hemolytic cocci. Optochin resistant Viridans group strep live in the mouth, because
streptococci and bile insoluble. Normal flora of the they are not afraid of-the-chin (op-to-chin
oropharynx. resistant).
Streptococcus mutans and S mitis cause dental Sanguinis = blood. Think, “there is lots of
caries. blood in the heart” (endocarditis).
S sanguinis makes dextrans that bind to fibrin-
platelet aggregates on damaged heart valves,
causing subacute bacterial endocarditis.
Streptococcus Gram ⊕ cocci in chains A . Group A strep “Ph”yogenes pharyngitis can result in
pyogenes (group A cause: rheumatic “phever” and glomerulonephritis.
streptococci) Pyogenic—pharyngitis, cellulitis, impetigo Strains causing impetigo can induce
A (“honey-crusted” lesions), erysipelas glomerulonephritis.
Toxigenic—scarlet fever, toxic shock–like Scarlet fever—blanching, sandpaper-like body
syndrome, necrotizing fasciitis rash, strawberry tongue, and circumoral
Immunologic—rheumatic fever, pallor in the setting of group A streptococcal
glomerulonephritis pharyngitis (erythrogenic toxin ⊕).
Bacitracin sensitive, β-hemolytic, pyrrolidonyl
arylamidase (PYR) ⊕. Hyaluronic acid capsule
and M protein inhibit phagocytosis. Antibodies
to M protein enhance host defenses against S
pyogenes but can give rise to rheumatic fever.
ASO titer or anti-DNase B antibodies indicate
recent S pyogenes infection.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 136 11/14/19 12:20 PM