Page 181 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 181
Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology Microbiology ` microbiology—cliNical bacteriology SEcTioN ii 137
Streptococcus Gram ⊕ cocci, bacitracin resistant, β-hemolytic, Group B for Babies!
agalactiae (group B colonizes vagina; causes pneumonia,
streptococci) meningitis, and sepsis, mainly in babies.
Produces CAMP factor, which enlarges the
area of hemolysis formed by S aureus. (Note:
CAMP stands for the authors of the test, not
cyclic AMP.) Hippurate test ⊕. PYR ⊝.
Screen pregnant women at 35–37 weeks of
gestation with rectal and vaginal swabs.
Patients with ⊕ culture receive intrapartum
penicillin/ampicillin prophylaxis.
Streptococcus bovis Gram ⊕ cocci, colonizes the gut. S gallolyticus Bovis in the blood = cancer in the colon.
(S bovis biotype 1) can cause bacteremia and
subacute endocarditis and is associated with
colon cancer.
Enterococci Gram ⊕ cocci. Enterococci (E faecalis and Enterococci are more resilient than
E faecium) are normal colonic flora that are streptococci, can grow in 6.5% NaCl and bile
penicillin G resistant and cause UTI, biliary (lab test).
tract infections, and subacute endocarditis Entero = intestine, faecalis = feces, strepto =
(following GI/GU procedures). Catalase ⊝, twisted (chains), coccus = berry.
PYR ⊕, variable hemolysis.
VRE (vancomycin-resistant enterococci) are an
important cause of nosocomial infection.
Bacillus anthracis Gram ⊕, spore-forming rod that produces anthrax toxin (an exotoxin consisting of protective
antigen, lethal factor, and edema factor). Has a polypeptide capsule (poly d-glutamate). Colonies
show a halo of projections, sometimes referred to as “medusa head” appearance.
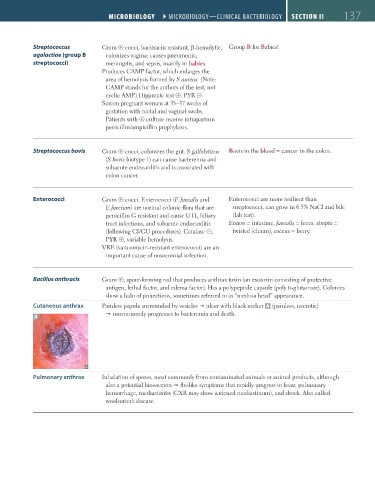
Cutaneous anthrax Painless papule surrounded by vesicles ulcer with black eschar A (painless, necrotic)
A uncommonly progresses to bacteremia and death.
Pulmonary anthrax Inhalation of spores, most commonly from contaminated animals or animal products, although
also a potential bioweapon flu-like symptoms that rapidly progress to fever, pulmonary
hemorrhage, mediastinitis (CXR may show widened mediastinum), and shock. Also called
woolsorter’s disease.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 137 11/14/19 12:20 PM