Page 300 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 300
256 SectiOn ii Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS
` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS
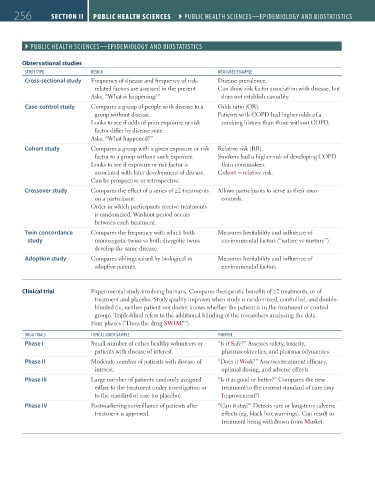
Observational studies
STUdy TyPE dESIgN mEASURES/EXAmPLE
Cross-sectional study Frequency of disease and frequency of risk- Disease prevalence.
related factors are assessed in the present. Can show risk factor association with disease, but
Asks, “What is happening?” does not establish causality.
Case-control study Compares a group of people with disease to a Odds ratio (OR).
group without disease. Patients with COPD had higher odds of a
Looks to see if odds of prior exposure or risk smoking history than those without COPD.
factor differ by disease state.
Asks, “What happened?”
Cohort study Compares a group with a given exposure or risk Relative risk (RR).
factor to a group without such exposure. Smokers had a higher risk of developing COPD
Looks to see if exposure or risk factor is than nonsmokers.
associated with later development of disease. Cohort = relative risk.
Can be prospective or retrospective.
Crossover study Compares the effect of a series of ≥2 treatments Allows participants to serve as their own
on a participant. controls.
Order in which participants receive treatments
is randomized. Washout period occurs
between each treatment.
Twin concordance Compares the frequency with which both Measures heritability and influence of
study monozygotic twins vs both dizygotic twins environmental factors (“nature vs nurture”).
develop the same disease.
Adoption study Compares siblings raised by biological vs Measures heritability and influence of
adoptive parents. environmental factors.
Clinical trial Experimental study involving humans. Compares therapeutic benefits of ≥2 treatments, or of
treatment and placebo. Study quality improves when study is randomized, controlled, and double-
blinded (ie, neither patient nor doctor knows whether the patient is in the treatment or control
group). Triple-blind refers to the additional blinding of the researchers analyzing the data.
Four phases (“Does the drug SWIM?”).
dRUg TRIALS TyPICAL STUdy SAmPLE PURPoSE
Phase I Small number of either healthy volunteers or “Is it Safe?” Assesses safety, toxicity,
patients with disease of interest. pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics.
Phase II Moderate number of patients with disease of “Does it Work?” Assesses treatment efficacy,
interest. optimal dosing, and adverse effects.
Phase III Large number of patients randomly assigned “Is it as good or better?” Compares the new
either to the treatment under investigation or treatment to the current standard of care (any
to the standard of care (or placebo). Improvement?).
Phase IV Postmarketing surveillance of patients after “Can it stay?” Detects rare or long-term adverse
treatment is approved. effects (eg, black box warnings). Can result in
treatment being withdrawn from Market.
FAS1_2019_06-PubHealth.indd 256 11/7/19 4:16 PM