Page 305 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 305
Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS SectiOn ii 261
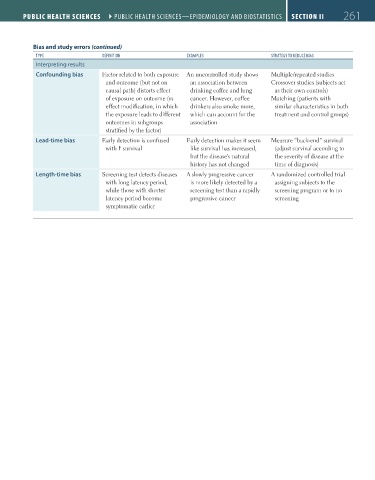
Bias and study errors (continued)
TyPE dEFINITIoN EXAmPLES STRATEgy To REdUCE BIAS
Interpreting results
Confounding bias Factor related to both exposure An uncontrolled study shows Multiple/repeated studies
and outcome (but not on an association between Crossover studies (subjects act
causal path) distorts effect drinking coffee and lung as their own controls)
of exposure on outcome (vs cancer. However, coffee Matching (patients with
effect modification, in which drinkers also smoke more, similar characteristics in both
the exposure leads to different which can account for the treatment and control groups)
outcomes in subgroups association
stratified by the factor)
Lead-time bias Early detection is confused Early detection makes it seem Measure “back-end” survival
with survival like survival has increased, (adjust survival according to
but the disease’s natural the severity of disease at the
history has not changed time of diagnosis)
Length-time bias Screening test detects diseases A slowly progressive cancer A randomized controlled trial
with long latency period, is more likely detected by a assigning subjects to the
while those with shorter screening test than a rapidly screening program or to no
latency period become progressive cancer screening
symptomatic earlier
FAS1_2019_06-PubHealth.indd 261 11/7/19 4:16 PM