Page 304 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 304
260 SectiOn ii Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS
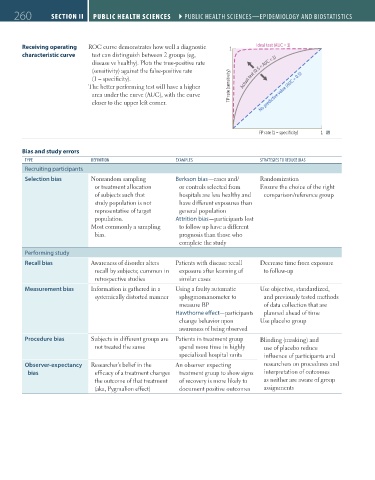
Receiving operating ROC curve demonstrates how well a diagnostic 1 Ideal test (AUC = 1)
characteristic curve test can distinguish between 2 groups (eg,
disease vs healthy). Plots the true-positive rate
(sensitivity) against the false-positive rate
(1 – specificity). Actual test (0.5 < AUC < 1)
The better performing test will have a higher TP rate (sensitivity)
area under the curve (AUC), with the curve No predictive value (AUC = 0.5)
closer to the upper left corner.
FP rate (1 – specificity) 1
Bias and study errors
TyPE dEFINITIoN EXAmPLES STRATEgIES To REdUCE BIAS
Recruiting participants
Selection bias Nonrandom sampling Berkson bias—cases and/ Randomization
or treatment allocation or controls selected from Ensure the choice of the right
of subjects such that hospitals are less healthy and comparison/reference group
study population is not have different exposures than
representative of target general population
population. Attrition bias—participants lost
Most commonly a sampling to follow up have a different
bias. prognosis than those who
complete the study
Performing study
Recall bias Awareness of disorder alters Patients with disease recall Decrease time from exposure
recall by subjects; common in exposure after learning of to follow-up
retrospective studies similar cases
Measurement bias Information is gathered in a Using a faulty automatic Use objective, standardized,
systemically distorted manner sphygmomanometer to and previously tested methods
measure BP of data collection that are
Hawthorne effect—participants planned ahead of time
change behavior upon Use placebo group
awareness of being observed
Procedure bias Subjects in different groups are Patients in treatment group Blinding (masking) and
not treated the same spend more time in highly use of placebo reduce
specialized hospital units influence of participants and
Observer-expectancy Researcher’s belief in the An observer expecting researchers on procedures and
bias efficacy of a treatment changes treatment group to show signs interpretation of outcomes
the outcome of that treatment of recovery is more likely to as neither are aware of group
(aka, Pygmalion effect) document positive outcomes assignments
FAS1_2019_06-PubHealth.indd 260 11/7/19 4:16 PM