Page 301 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 301
Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS SectiOn ii 257
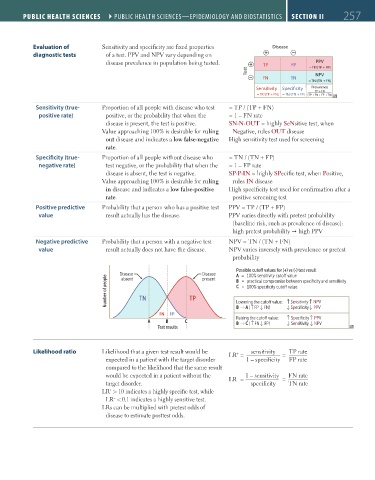
Evaluation of Sensitivity and specificity are fixed properties Disease
diagnostic tests of a test. PPV and NPV vary depending on –
disease prevalence in population being tested. TP FP PPV
Test = TP/(TP + FP)
– FN TN NPV
= TN/(TN + FN)
Sensitivity Speci city Prevalence
TP + FN
= TP/(TP + FN) = TN/(TN + FP) (TP + FN + FP + TN)
Sensitivity (true- Proportion of all people with disease who test = TP / (TP + FN)
positive rate) positive, or the probability that when the = 1 – FN rate
disease is present, the test is positive. SN-N-OUT = highly SeNsitive test, when
Value approaching 100% is desirable for ruling Negative, rules OUT disease
out disease and indicates a low false-negative High sensitivity test used for screening
rate.
Specificity (true- Proportion of all people without disease who = TN / (TN + FP)
negative rate) test negative, or the probability that when the = 1 – FP rate
disease is absent, the test is negative. SP-P-IN = highly SPecific test, when Positive,
Value approaching 100% is desirable for ruling rules IN disease
in disease and indicates a low false-positive High specificity test used for confirmation after a
rate. positive screening test
Positive predictive Probability that a person who has a positive test PPV = TP / (TP + FP)
value result actually has the disease. PPV varies directly with pretest probability
(baseline risk, such as prevalence of disease):
high pretest probability high PPV
Negative predictive Probability that a person with a negative test NPV = TN / (TN + FN)
value result actually does not have the disease. NPV varies inversely with prevalence or pretest
probability
Possible cuto values for (+) vs (-) test result
Disease Disease A = 100% sensitivity cuto value
Number of people TN TP C Lowering the cuto value: ↑ Sensitivity ↑ NPV
absent
present
B = practical compromise between specificity and sensitivity
= 100% specificity cuto value
↑
↑
↑
↑
FN FP B A (↑ FP FN) Specificity PPV
A B C Raising the cuto value: ↑ Specificity ↑ PPV
B C (↑ FN FP) Sensitivity NPV
Test results
↑
↑
↑
↑
Likelihood ratio Likelihood that a given test result would be LR = = TP rate
+ sensitivity
expected in a patient with the target disorder 1 – specificity FP rate
compared to the likelihood that the same result
would be expected in a patient without the LR = 1 – sensitivity FN rate
–
=
target disorder. specificity TN rate
+
LR > 10 indicates a highly specific test, while
–
LR < 0.1 indicates a highly sensitive test.
LRs can be multiplied with pretest odds of
disease to estimate posttest odds.
FAS1_2019_06-PubHealth.indd 257 11/7/19 4:16 PM