Page 302 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 302
a/c ad
Odds ratio = =
b/d bc
a/(a + b)
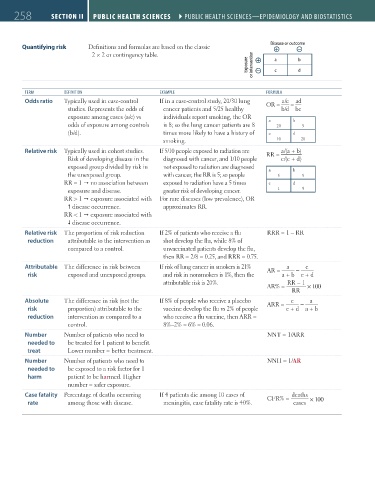
258 SectiOn ii Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS
Relative risk =
c/(c + d)
a c
Attributable risk =
a + b c + d
Disease or outcome
Quantifying risk Definitions and formulas are based on the classic
2 × 2 or contingency table. a b
Exposure or intervention c d
TERm dEFINITIoN EXAmPLE FoRmULA
Odds ratio Typically used in case-control If in a case-control study, 20/30 lung OR = a/c ad
=
studies. Represents the odds of cancer patients and 5/25 healthy b/d bc
exposure among cases (a/c) vs individuals report smoking, the OR a b
odds of exposure among controls is 8; so the lung cancer patients are 8 20 5
(b/d). times more likely to have a history of c d
smoking. 10 20
Relative risk Typically used in cohort studies. If 5/10 people exposed to radiation are RR = a/(a + b)
Risk of developing disease in the diagnosed with cancer, and 1/10 people c/(c + d)
exposed group divided by risk in not exposed to radiation are diagnosed a b
the unexposed group. with cancer, the RR is 5; so people 5 5
RR = 1 no association between exposed to radiation have a 5 times c d
exposure and disease. greater risk of developing cancer. 1 9
RR > 1 exposure associated with For rare diseases (low prevalence), OR
disease occurrence. approximates RR.
RR < 1 exposure associated with
disease occurrence.
Relative risk The proportion of risk reduction If 2% of patients who receive a flu RRR = 1 − RR
reduction attributable to the intervention as shot develop the flu, while 8% of
compared to a control. unvaccinated patients develop the flu,
then RR = 2/8 = 0.25, and RRR = 0.75.
Attributable The difference in risk between If risk of lung cancer in smokers is 21% AR = a − c
risk exposed and unexposed groups. and risk in nonsmokers is 1%, then the a + b c + d
attributable risk is 20%. RR − 1
AR% = × 100
RR
Absolute The difference in risk (not the If 8% of people who receive a placebo ARR = c − a
risk proportion) attributable to the vaccine develop the flu vs 2% of people c + d a + b
reduction intervention as compared to a who receive a flu vaccine, then ARR =
control. 8%–2% = 6% = 0.06.
Number Number of patients who need to NNT = 1/ARR
needed to be treated for 1 patient to benefit.
treat Lower number = better treatment.
Number Number of patients who need to NNH = 1/AR
needed to be exposed to a risk factor for 1
harm patient to be harmed. Higher
number = safer exposure.
Case fatality Percentage of deaths occurring If 4 patients die among 10 cases of CFR% = deaths
rate among those with disease. meningitis, case fatality rate is 40%. cases × 100
FAS1_2019_06-PubHealth.indd 258 11/7/19 4:16 PM