Page 307 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 307
Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS Public HealtH ScienceS ` PUBLIC HEALTH SCIENCES—EPIdEmIoLogy ANd BIoSTATISTICS SectiOn ii 263
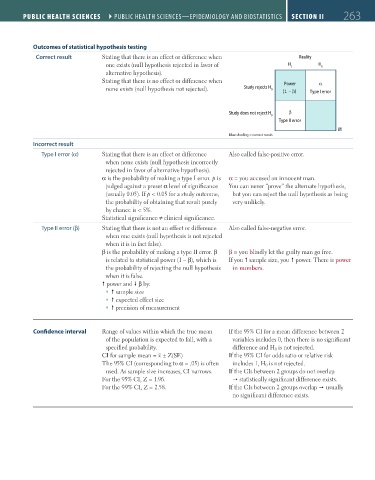
Outcomes of statistical hypothesis testing
Correct result Stating that there is an effect or difference when Reality
one exists (null hypothesis rejected in favor of H 1 H 0
alternative hypothesis).
Stating that there is no effect or difference when Power α
none exists (null hypothesis not rejected). Study rejects H 0 (1 – β) Type I error
Study does not reject H 0 β
Type II error
Blue shading = correct result.
Incorrect result
Type I error (α) Stating that there is an effect or difference Also called false-positive error.
when none exists (null hypothesis incorrectly
rejected in favor of alternative hypothesis).
α is the probability of making a type I error. p is α = you accused an innocent man.
judged against a preset α level of significance You can never “prove” the alternate hypothesis,
(usually 0.05). If p < 0.05 for a study outcome, but you can reject the null hypothesis as being
the probability of obtaining that result purely very unlikely.
by chance is < 5%.
Statistical significance ≠ clinical significance.
Type II error (β) Stating that there is not an effect or difference Also called false-negative error.
when one exists (null hypothesis is not rejected
when it is in fact false).
β is the probability of making a type II error. β β = you blindly let the guilty man go free.
is related to statistical power (1 – β), which is If you sample size, you power. There is power
the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis in numbers.
when it is false.
power and β by:
sample size
expected effect size
precision of measurement
Confidence interval Range of values within which the true mean If the 95% CI for a mean difference between 2
of the population is expected to fall, with a variables includes 0, then there is no significant
specified probability. difference and H 0 is not rejected.
CI for sample mean = x¯ ± Z(SE) If the 95% CI for odds ratio or relative risk
The 95% CI (corresponding to α = .05) is often includes 1, H 0 is not rejected.
used. As sample size increases, CI narrows. If the CIs between 2 groups do not overlap
For the 95% CI, Z = 1.96. statistically significant difference exists.
For the 99% CI, Z = 2.58. If the CIs between 2 groups overlap usually
no significant difference exists.
FAS1_2019_06-PubHealth.indd 263 11/7/19 4:16 PM