Page 333 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 333
CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PHYSIOlOGY SECTION III 289
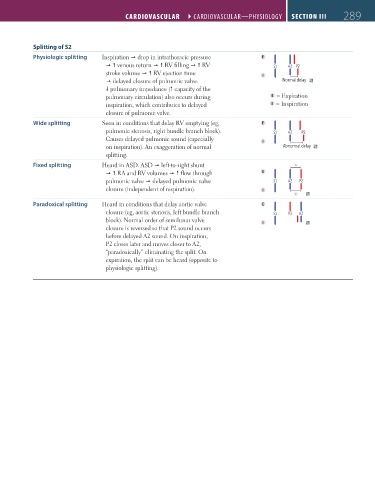
Splitting of S2
Physiologic splitting Inspiration drop in intrathoracic pressure E
venous return RV filling RV S1 A2 P2
stroke volume RV ejection time I
delayed closure of pulmonic valve. Normal delay
pulmonary impedance ( capacity of the
pulmonary circulation) also occurs during E = Expiration
inspiration, which contributes to delayed I = Inspiration
closure of pulmonic valve.
Wide splitting Seen in conditions that delay RV emptying (eg, E
pulmonic stenosis, right bundle branch block). S1 A2 P2
Causes delayed pulmonic sound (especially I
on inspiration). An exaggeration of normal Abnormal delay
splitting.
Fixed splitting Heard in ASD. ASD left-to-right shunt =
RA and RV volumes flow through E
pulmonic valve delayed pulmonic valve S1 A2 P2
closure (independent of respiration). I
=
Paradoxical splitting Heard in conditions that delay aortic valve E
closure (eg, aortic stenosis, left bundle branch S1 P2 P2 A2 A2 A2 A2
block). Normal order of semilunar valve I
closure is reversed so that P2 sound occurs
before delayed A2 sound. On inspiration,
P2 closes later and moves closer to A2,
“paradoxically” eliminating the split. On
expiration, the split can be heard (opposite to
physiologic splitting).
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 289 11/7/19 4:24 PM