Page 350 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 350
306 SECTION III CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY CARDIOvASCuLAR ``CARdIOvASCulAR—PATHOlOGY
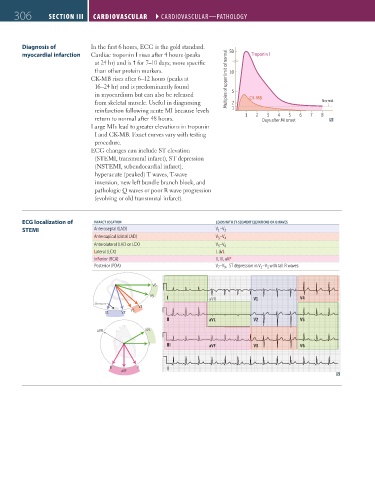
Diagnosis of In the first 6 hours, ECG is the gold standard.
myocardial infarction Cardiac troponin I rises after 4 hours (peaks 50 Troponin I
at 24 hr) and is for 7–10 days; more specific
than other protein markers. 10
CK-MB rises after 6–12 hours (peaks at Multiples of upper limit of normal
16–24 hr) and is predominantly found
in myocardium but can also be released 5
from skeletal muscle. Useful in diagnosing 2 CK-MB Normal
reinfarction following acute MI because levels 1
4
3
5
return to normal after 48 hours. 1 2 Days after MI onset 6 7 8
Large MIs lead to greater elevations in troponin
I and CK-MB. Exact curves vary with testing
procedure.
ECG changes can include ST elevation
(STEMI, transmural infarct), ST depression
(NSTEMI, subendocardial infarct),
hyperacute (peaked) T waves, T-wave
inversion, new left bundle branch block, and
pathologic Q waves or poor R wave progression
(evolving or old transmural infarct).
ECG localization of INFARCT LOCATION LEADS WITH ST-SEGMENT ELEVATIONS OR Q WAVES
STEMI Anteroseptal (LAD) V –V 2
1
Anteroapical (distal LAD) V –V 4
3
Anterolateral (LAD or LCX) V 5 –V 6
Lateral (LCX) I, aVL
InFerior (RCA) II, III, aVF
Posterior (PDA) V –V , ST depression in V –V with tall R waves
1
9
7
3
V6
V5 I aVR V1 V4
Sternum
V4
V3
V1 V2
II aVL V2 V5
aVR aVL
I III aVF V3 V6
III II II
aVF
FAS1_2019_07-Cardio.indd 306 11/7/19 4:24 PM