Page 435 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 435
Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology Gastrointestinal ` gastrointestinal—PatHology seCtion iii 391
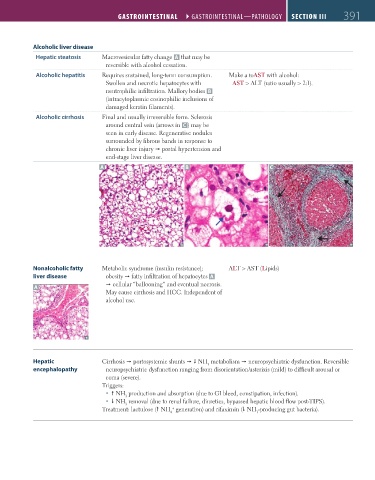
Alcoholic liver disease
Hepatic steatosis Macrovesicular fatty change A that may be
reversible with alcohol cessation.
Alcoholic hepatitis Requires sustained, long-term consumption. Make a toAST with alcohol:
Swollen and necrotic hepatocytes with AST > ALT (ratio usually > 2:1).
neutrophilic infiltration. Mallory bodies B
(intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions of
damaged keratin filaments).
Alcoholic cirrhosis Final and usually irreversible form. Sclerosis
around central vein (arrows in C ) may be
seen in early disease. Regenerative nodules
surrounded by fibrous bands in response to
chronic liver injury portal hypertension and
end-stage liver disease.
A B C
Nonalcoholic fatty Metabolic syndrome (insulin resistance); ALT > AST (Lipids)
liver disease obesity fatty infiltration of hepatocytes A
A cellular “ballooning” and eventual necrosis.
May cause cirrhosis and HCC. Independent of
alcohol use.
Hepatic Cirrhosis portosystemic shunts NH metabolism neuropsychiatric dysfunction. Reversible
3
encephalopathy neuropsychiatric dysfunction ranging from disorientation/asterixis (mild) to difficult arousal or
coma (severe).
Triggers:
NH production and absorption (due to GI bleed, constipation, infection).
3
NH removal (due to renal failure, diuretics, bypassed hepatic blood flow post-TIPS).
3
Treatment: lactulose ( NH generation) and rifaximin ( NH -producing gut bacteria).
+
3
4
FAS1_2019_09-Gastrointestinal.indd 391 11/7/19 4:42 PM