Page 507 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 507
Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` pathology section iii 463
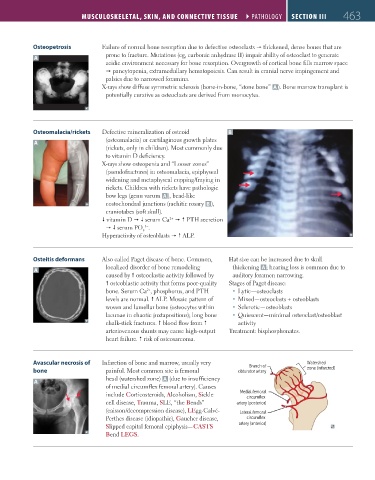
Osteopetrosis Failure of normal bone resorption due to defective osteoclasts thickened, dense bones that are
A prone to fracture. Mutations (eg, carbonic anhydrase II) impair ability of osteoclast to generate
acidic environment necessary for bone resorption. Overgrowth of cortical bone fills marrow space
pancytopenia, extramedullary hematopoiesis. Can result in cranial nerve impingement and
palsies due to narrowed foramina.
X-rays show diffuse symmetric sclerosis (bone-in-bone, “stone bone” A ). Bone marrow transplant is
potentially curative as osteoclasts are derived from monocytes.
Osteomalacia/rickets Defective mineralization of osteoid B
(osteomalacia) or cartilaginous growth plates
A
(rickets, only in children). Most commonly due
to vitamin D deficiency.
X-rays show osteopenia and “Looser zones”
(pseudofractures) in osteomalacia, epiphyseal
widening and metaphyseal cupping/fraying in
rickets. Children with rickets have pathologic
bow legs (genu varum A ), bead-like
costochondral junctions (rachitic rosary B ),
craniotabes (soft skull).
vitamin D serum Ca PTH secretion
2+
serum PO .
3−
4
Hyperactivity of osteoblasts ALP.
Osteitis deformans Also called Paget disease of bone. Common, Hat size can be increased due to skull
localized disorder of bone remodeling thickening A ; hearing loss is common due to
A
caused by osteoclastic activity followed by auditory foramen narrowing.
osteoblastic activity that forms poor-quality Stages of Paget disease:
bone. Serum Ca , phosphorus, and PTH Lytic—osteoclasts
2+
levels are normal. ALP. Mosaic pattern of Mixed—osteoclasts + osteoblasts
woven and lamellar bone (osteocytes within Sclerotic—osteoblasts
lacunae in chaotic juxtapositions); long bone Quiescent—minimal osteoclast/osteoblast
chalk-stick fractures. blood flow from activity
arteriovenous shunts may cause high-output Treatment: bisphosphonates.
heart failure. risk of osteosarcoma.
Avascular necrosis of Infarction of bone and marrow, usually very Branch of Watershed
bone painful. Most common site is femoral obturator artery zone (infarcted)
A head (watershed zone) A (due to insufficiency
of medial circumflex femoral artery). Causes
include Corticosteroids, Alcoholism, Sickle Medial femoral
circumflex
cell disease, Trauma, SLE, “the Bends” artery (posterior)
(caisson/decompression disease), LEgg-Calvé- Lateral femoral
Perthes disease (idiopathic), Gaucher disease, circumflex
Slipped capital femoral epiphysis—CASTS artery (anterior)
Bend LEGS.
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 463 11/7/19 5:23 PM