Page 586 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 586
542 SecTioN iii Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—oPhthAlmology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—oPhthAlmology
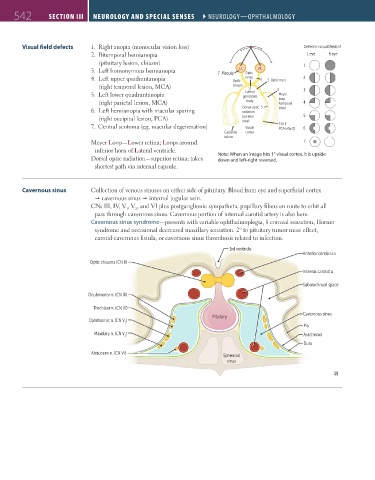
Visual field defects 1. Right anopia (monocular vision loss) Defect in visual field of
2. Bitemporal hemianopia L eye R eye
(pituitary lesion, chiasm) 1
3. Left homonymous hemianopia 7 Macula Lt. Optic Rt.
4. Left upper quadrantanopia Optic nerve 1 3 Optic tract 2
(right temporal lesion, MCA) chiasm 2 4
Lateral
5. Left lower quadrantanopia geniculate Meyer 3
(right parietal lesion, MCA) body loop 4
(temporal
6. Left hemianopia with macular sparing Dorsal optic 5 lobe)
radiation
(right occipital lesion, PCA) (parietal 5
lobe)
7. Central scotoma (eg, macular degeneration) Visual 3 (6 if 6
PCA infarct)
Calcarine cortex
sulcus
Meyer Loop—Lower retina; Loops around 7
inferior horn of Lateral ventricle.
Dorsal optic radiation—superior retina; takes Note: When an image hits 1° visual cortex, it is upside
down and left-right reversed.
shortest path via internal capsule.
Cavernous sinus Collection of venous sinuses on either side of pituitary. Blood from eye and superficial cortex
cavernous sinus internal jugular vein.
CNs III, IV, V , V , and VI plus postganglionic sympathetic pupillary fibers en route to orbit all
1 2
pass through cavernous sinus. Cavernous portion of internal carotid artery is also here.
Cavernous sinus syndrome—presents with variable ophthalmoplegia, corneal sensation, Horner
syndrome and occasional decreased maxillary sensation. 2° to pituitary tumor mass effect,
carotid-cavernous fistula, or cavernous sinus thrombosis related to infection.
3rd ventricle
Anterior cerebral a.
Optic chiasma (CN II)
Internal carotid a.
Subarachnoid space
Oculomotor n. (CN III)
Trochlear n. (CN IV)
Cavernous sinus
Pituitary
Ophthalmic n. (CN V )
1
Pia
Maxillary n. (CN V ) Arachnoid
2
Dura
Abducens n. (CN VI)
Sphenoid
sinus
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 542 11/8/19 7:39 AM