Page 639 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 639
Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy Renal ` RENAL—PAthoLogy SeCTIOn III 595
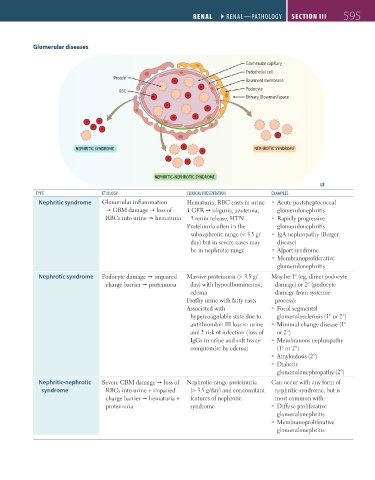
Glomerular diseases
Glomerular capillary
Endothelial cell
Protein
Basement membrane
Podocyte
RBC
Urinary (Bowman) space
NEPHRITIC SYNDROME NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
NEPHRITIC-NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
tyPE EtioLogy CLiNiCAL PREsENtAtioN EXAmPLEs
Nephritic syndrome Glomerular inflammation Hematuria, RBC casts in urine Acute poststreptococcal
GBM damage loss of GFR oliguria, azotemia, glomerulonephritis
RBCs into urine hematuria renin release, HTN Rapidly progressive
Proteinuria often in the glomerulonephritis
subnephrotic range (< 3.5 g/ IgA nephropathy (Berger
day) but in severe cases may disease)
be in nephrotic range Alport syndrome
Membranoproliferative
glomerulonephritis
Nephrotic syndrome Podocyte damage impaired Massive proteinuria (> 3.5 g/ May be 1° (eg, direct podocyte
charge barrier proteinuria day) with hypoalbuminemia, damage) or 2° (podocyte
edema damage from systemic
Frothy urine with fatty casts process):
Associated with Focal segmental
hypercoagulable state due to glomerulosclerosis (1° or 2°)
antithrombin III loss in urine Minimal change disease (1°
and risk of infection (loss of or 2°)
IgGs in urine and soft tissue Membranous nephropathy
compromise by edema) (1° or 2°)
Amyloidosis (2°)
Diabetic
glomerulonephropathy (2°)
Nephritic-nephrotic Severe GBM damage loss of Nephrotic-range proteinuria Can occur with any form of
syndrome RBCs into urine + impaired (> 3.5 g/day) and concomitant nephritic syndrome, but is
charge barrier hematuria + features of nephrotic most common with:
proteinuria syndrome Diffuse proliferative
glomerulonephritis
Membranoproliferative
glomerulonephritis
FAS1_2019_14-Renal.indd 595 11/7/19 5:42 PM