Page 702 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 702
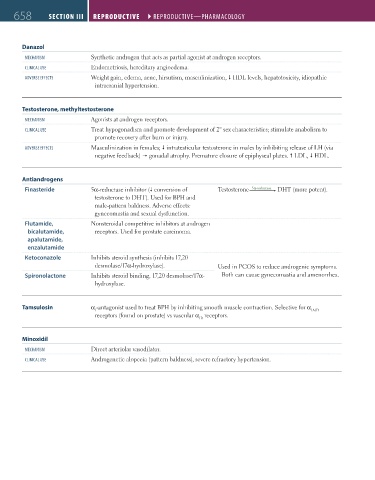
658 SectioN iii RepRoductive ` REPRODUCTIVE—PHARmACOlOgy
Danazol
mECHANISm Synthetic androgen that acts as partial agonist at androgen receptors.
ClINICAl USE Endometriosis, hereditary angioedema.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Weight gain, edema, acne, hirsutism, masculinization, HDL levels, hepatotoxicity, idiopathic
intracranial hypertension.
Testosterone, methyltestosterone
mECHANISm Agonists at androgen receptors.
ClINICAl USE Treat hypogonadism and promote development of 2° sex characteristics; stimulate anabolism to
promote recovery after burn or injury.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Masculinization in females; intratesticular testosterone in males by inhibiting release of LH (via
negative feedback) gonadal atrophy. Premature closure of epiphyseal plates. LDL, HDL.
Antiandrogens
Finasteride 5α-reductase inhibitor ( conversion of Testosterone 5α-reductase DHT (more potent).
testosterone to DHT). Used for BPH and
male-pattern baldness. Adverse effects:
gynecomastia and sexual dysfunction.
Flutamide, Nonsteroidal competitive inhibitors at androgen
bicalutamide, receptors. Used for prostate carcinoma.
apalutamide,
enzalutamide
Ketoconazole Inhibits steroid synthesis (inhibits 17,20
desmolase/17α-hydroxylase). Used in PCOS to reduce androgenic symptoms.
Spironolactone Inhibits steroid binding, 17,20 desmolase/17α- Both can cause gynecomastia and amenorrhea.
hydroxylase.
Tamsulosin α -antagonist used to treat BPH by inhibiting smooth muscle contraction. Selective for α
1 1A/D
receptors (found on prostate) vs vascular α receptors.
1B
Minoxidil
mECHANISm Direct arteriolar vasodilator.
ClINICAl USE Androgenetic alopecia (pattern baldness), severe refractory hypertension.
FAS1_2019_15-Repro.indd 658 11/7/19 5:52 PM