Page 705 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 705
RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—EmbRYOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—EmbRYOlOgY seCtioN iii 661
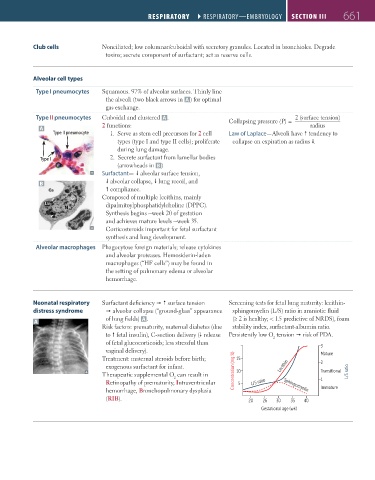
Club cells Nonciliated; low columnar/cuboidal with secretory granules. Located in bronchioles. Degrade
toxins; secrete component of surfactant; act as reserve cells.
Alveolar cell types
Type I pneumocytes Squamous. 97% of alveolar surfaces. Thinly line
the alveoli (two black arrows in A ) for optimal
gas exchange.
Type II pneumocytes Cuboidal and clustered A . 2 (surface tension)
Collapsing pressure (P) =
A 2 functions: radius
Type II pneumocyte 1. Serve as stem cell precursors for 2 cell Law of Laplace—Alveoli have tendency to
types (type I and type II cells); proliferate collapse on expiration as radius .
during lung damage.
Type I 2. Secrete surfactant from lamellar bodies
(arrowheads in B )
Surfactant— alveolar surface tension,
B alveolar collapse, lung recoil, and
compliance.
Composed of multiple lecithins, mainly
dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC).
Synthesis begins ~week 20 of gestation
and achieves mature levels ~week 35.
Corticosteroids important for fetal surfactant
synthesis and lung development.
Alveolar macrophages Phagocytose foreign materials; release cytokines
and alveolar proteases. Hemosiderin-laden
macrophages (“HF cells”) may be found in
the setting of pulmonary edema or alveolar
hemorrhage.
Neonatal respiratory Surfactant deficiency surface tension Screening tests for fetal lung maturity: lecithin-
distress syndrome alveolar collapse (“ground-glass” appearance sphingomyelin (L/S) ratio in amniotic fluid
of lung fields) A . (≥ 2 is healthy; < 1.5 predictive of NRDS), foam
A
Risk factors: prematurity, maternal diabetes (due stability index, surfactant-albumin ratio.
to fetal insulin), C-section delivery ( release Persistently low O tension risk of PDA.
2
of fetal glucocorticoids; less stressful than 3
vaginal delivery). Mature
Treatment: maternal steroids before birth; 15
exogenous surfactant for infant. Lecithin 2
Therapeutic supplemental O can result in Concentration (mg %) 10 Transitional L/S ratio
2
Retinopathy of prematurity, Intraventricular 5 L/S ratio Sphingomyelin 1
hemorrhage, Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Immature
(RIB). 20 26 30 35 40
Gestational age (wk)
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 661 11/8/19 7:33 AM