Page 708 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 708
664 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY
` RESPIRATORY—PhYSIOlOgY
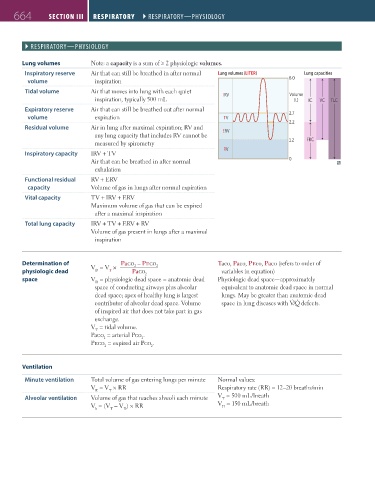
Lung volumes Note: a capacity is a sum of ≥ 2 physiologic volumes.
Inspiratory reserve Air that can still be breathed in after normal Lung volumes (LITER) Lung capacities
volume inspiration 6.0
Tidal volume Air that moves into lung with each quiet Volume
inspiration, typically 500 mL IRV (L) IC VC TLC
Expiratory reserve Air that can still be breathed out after normal
volume expiration TV 2.7
2.2
Residual volume Air in lung after maximal expiration; RV and
any lung capacity that includes RV cannot be ERV
measured by spirometry 1.2 FRC
RV
Inspiratory capacity IRV + TV
Air that can be breathed in after normal 0
exhalation
Functional residual RV + ERV
capacity Volume of gas in lungs after normal expiration
Vital capacity TV + IRV + ERV
Maximum volume of gas that can be expired
after a maximal inspiration
Total lung capacity IRV + TV + ERV + RV
Volume of gas present in lungs after a maximal
inspiration
Determination of V = V × Paco – Peco Taco, Paco, Peco, Paco (refers to order of
2
2
physiologic dead D T Paco 2 variables in equation)
space V = physiologic dead space = anatomic dead Physiologic dead space—approximately
D
space of conducting airways plus alveolar equivalent to anatomic dead space in normal
dead space; apex of healthy lung is largest lungs. May be greater than anatomic dead
˙ ˙
contributor of alveolar dead space. Volume space in lung diseases with V/Q defects.
of inspired air that does not take part in gas
exchange.
V = tidal volume.
T
Paco = arterial Pco .
2
2
Peco = expired air Pco .
2
2
Ventilation
Minute ventilation Total volume of gas entering lungs per minute Normal values:
V = V × RR Respiratory rate (RR) = 12–20 breaths/min
E T
Alveolar ventilation Volume of gas that reaches alveoli each minute V = 500 mL/breath
T
V = (V − V ) × RR V = 150 mL/breath
D
A T D
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 664 11/8/19 7:34 AM