Page 729 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 729
RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY seCtioN iii 685
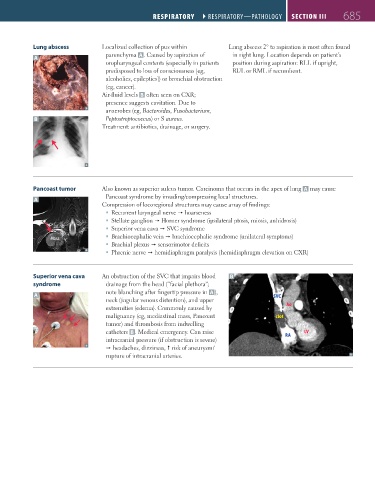
Lung abscess Localized collection of pus within Lung abscess 2° to aspiration is most often found
parenchyma A . Caused by aspiration of in right lung. Location depends on patient’s
A
oropharyngeal contents (especially in patients position during aspiration: RLL if upright,
predisposed to loss of consciousness [eg, RUL or RML if recumbent.
alcoholics, epileptics]) or bronchial obstruction
(eg, cancer).
Air-fluid levels B often seen on CXR;
presence suggests cavitation. Due to
anaerobes (eg, Bacteroides, Fusobacterium,
B Peptostreptococcus) or S aureus.
Treatment: antibiotics, drainage, or surgery.
Pancoast tumor Also known as superior sulcus tumor. Carcinoma that occurs in the apex of lung A may cause
A Pancoast syndrome by invading/compressing local structures.
Compression of locoregional structures may cause array of findings:
Recurrent laryngeal nerve hoarseness
Stellate ganglion Horner syndrome (ipsilateral ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis)
1st rib Superior vena cava SVC syndrome
Mass Brachiocephalic vein brachiocephalic syndrome (unilateral symptoms)
Brachial plexus sensorimotor deficits
Phrenic nerve hemidiaphragm paralysis (hemidiaphragm elevation on CXR)
Superior vena cava An obstruction of the SVC that impairs blood B
syndrome drainage from the head (“facial plethora”;
note blanching after fingertip pressure in A ),
A SVC
neck (jugular venous distention), and upper
extremities (edema). Commonly caused by Ao
malignancy (eg, mediastinal mass, Pancoast clot
tumor) and thrombosis from indwelling
catheters B . Medical emergency. Can raise LV
intracranial pressure (if obstruction is severe) RA
headaches, dizziness, risk of aneurysm/
rupture of intracranial arteries.
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 685 11/8/19 7:34 AM