Page 728 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 728
684 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY
Lung cancer Leading cause of cancer death. SPHERE of complications:
Presentation: cough, hemoptysis, bronchial Superior vena cava/thoracic outlet syndromes
obstruction, wheezing, pneumonic “coin” Pancoast tumor
lesion on CXR or noncalcified nodule on CT. Horner syndrome
Sites of metastases from lung cancer: Liver Endocrine (paraneoplastic)
(jaundice, hepatomegaly), Adrenals, Bone Recurrent laryngeal nerve compression
(pathologic fracture), Brain; “Lung ‘mets’ (hoarseness)
Love Affective Boneheads and Brainiacs.” Effusions (pleural or pericardial)
In the lung, metastases (usually multiple Risk factors include smoking, secondhand smoke,
lesions) are more common than 1° radon, asbestos, family history.
neoplasms. Most often from breast, colon, Squamous and Small cell carcinomas are Sentral
prostate, and bladder cancer. (central) and often caused by Smoking.
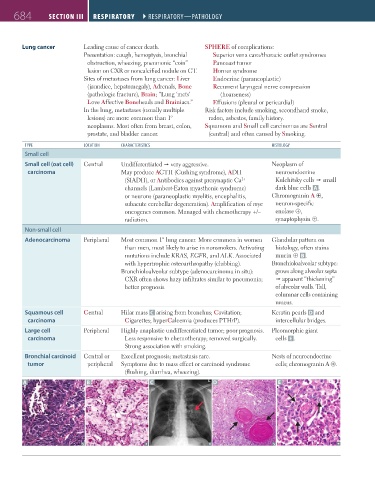
TYPE lOCATION ChARACTERISTICS hISTOlOgY
Small cell
Small cell (oat cell) Central Undifferentiated very aggressive. Neoplasm of
carcinoma May produce ACTH (Cushing syndrome), ADH neuroendocrine
(SIADH), or Antibodies against presynaptic Ca Kulchitsky cells small
2+
channels (Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome) dark blue cells A .
or neurons (paraneoplastic myelitis, encephalitis, Chromogranin A ⊕,
subacute cerebellar degeneration). Amplification of myc neuron-specific
oncogenes common. Managed with chemotherapy +/– enolase ⊕,
radiation. synaptophysin ⊕.
Non-small cell
Adenocarcinoma Peripheral Most common 1° lung cancer. More common in women Glandular pattern on
than men, most likely to arise in nonsmokers. Activating histology, often stains
mutations include KRAS, EGFR, and ALK. Associated mucin ⊕ B .
with hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (clubbing). Bronchioloalveolar subtype:
Bronchioloalveolar subtype (adenocarcinoma in situ): grows along alveolar septa
CXR often shows hazy infiltrates similar to pneumonia; apparent “thickening”
better prognosis. of alveolar walls. Tall,
columnar cells containing
mucus.
Squamous cell Central Hilar mass C arising from bronchus; Cavitation; Keratin pearls D and
carcinoma Cigarettes; hyperCalcemia (produces PTHrP). intercellular bridges.
Large cell Peripheral Highly anaplastic undifferentiated tumor; poor prognosis. Pleomorphic giant
carcinoma Less responsive to chemotherapy; removed surgically. cells E .
Strong association with smoking.
Bronchial carcinoid Central or Excellent prognosis; metastasis rare. Nests of neuroendocrine
tumor peripheral Symptoms due to mass effect or carcinoid syndrome cells; chromogranin A ⊕.
(flushing, diarrhea, wheezing).
A B C D E
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 684 11/8/19 7:34 AM