Page 727 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 727
RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY seCtioN iii 683
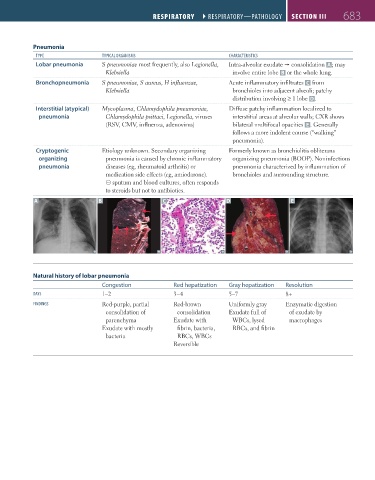
Pneumonia
TYPE TYPICAl ORgANISmS ChARACTERISTICS
Lobar pneumonia S pneumoniae most frequently, also Legionella, Intra-alveolar exudate consolidation A ; may
Klebsiella involve entire lobe B or the whole lung.
Bronchopneumonia S pneumoniae, S aureus, H influenzae, Acute inflammatory infiltrates C from
Klebsiella bronchioles into adjacent alveoli; patchy
distribution involving ≥ 1 lobe D.
Interstitial (atypical) Mycoplasma, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Diffuse patchy inflammation localized to
pneumonia Chlamydophila psittaci, Legionella, viruses interstitial areas at alveolar walls; CXR shows
(RSV, CMV, influenza, adenovirus) bilateral multifocal opacities E . Generally
follows a more indolent course (“walking”
pneumonia).
Cryptogenic Etiology unknown. Secondary organizing Formerly known as bronchiolitis obliterans
organizing pneumonia is caused by chronic inflammatory organizing pneumonia (BOOP). Noninfectious
pneumonia diseases (eg, rheumatoid arthritis) or pneumonia characterized by inflammation of
medication side effects (eg, amiodarone). bronchioles and surrounding structure.
⊝ sputum and blood cultures, often responds
to steroids but not to antibiotics.
A B C D E
Natural history of lobar pneumonia
Congestion Red hepatization Gray hepatization Resolution
DAYS 1–2 3–4 5–7 8+
FINDINgS Red-purple, partial Red-brown Uniformly gray Enzymatic digestion
consolidation of consolidation Exudate full of of exudate by
parenchyma Exudate with WBCs, lysed macrophages
Exudate with mostly fibrin, bacteria, RBCs, and fibrin
bacteria RBCs, WBCs
Reversible
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 683 11/8/19 7:34 AM