Page 724 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 724
680 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PAThOlOgY
Physical findings in select lung diseases
AbNORmAlITY bREATh SOUNDS PERCUSSION FREmITUS TRAChEAl DEVIATION
Pleural effusion Dull None if small
Away from side of lesion
if large
Atelectasis Dull Toward side of lesion
Simple pneumothorax Hyperresonant None
Tension Hyperresonant Away from side of lesion
pneumothorax
Consolidation Bronchial breath sounds; Dull None
(lobar pneumonia, late inspiratory crackles,
pulmonary edema) egophony, whispered
pectoriloquy
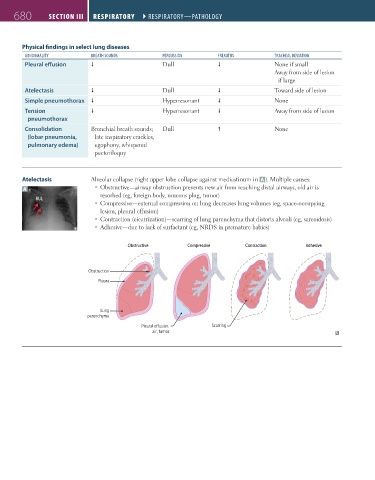
Atelectasis Alveolar collapse (right upper lobe collapse against mediastinum in A ). Multiple causes:
A Obstructive—airway obstruction prevents new air from reaching distal airways, old air is
resorbed (eg, foreign body, mucous plug, tumor)
RUL
Compressive—external compression on lung decreases lung volumes (eg, space-occupying
lesion, pleural effusion)
Contraction (cicatrization)—scarring of lung parenchyma that distorts alveoli (eg, sarcoidosis)
Adhesive—due to lack of surfactant (eg, NRDS in premature babies)
Obstructive Compressive Contraction Adhesive
Obstruction
Pleura
Lung
parenchyma
Pleural e usion, Scarring
air, tumor
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 680 11/8/19 7:34 AM