Page 730 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 730
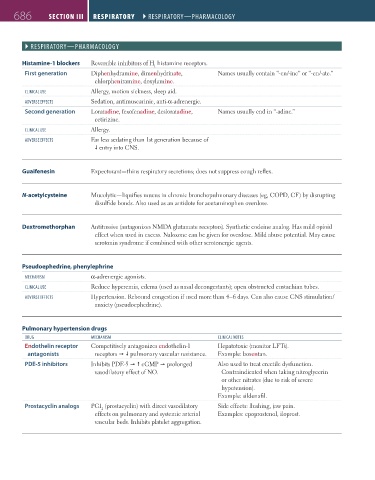
686 seCtioN iii RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhARmACOlOgY RespiRatoRy ` RESPIRATORY—PhARmACOlOgY
` RESPIRATORY—PhARmACOlOgY
Histamine-1 blockers Reversible inhibitors of H histamine receptors.
1
First generation Diphenhydramine, dimenhydrinate, Names usually contain “-en/-ine” or “-en/-ate.”
chlorpheniramine, doxylamine.
ClINICAl USE Allergy, motion sickness, sleep aid.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Sedation, antimuscarinic, anti-α-adrenergic.
Second generation Loratadine, fexofenadine, desloratadine, Names usually end in “-adine.”
cetirizine.
ClINICAl USE Allergy.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Far less sedating than 1st generation because of
entry into CNS.
Guaifenesin Expectorant—thins respiratory secretions; does not suppress cough reflex.
N-acetylcysteine Mucolytic—liquifies mucus in chronic bronchopulmonary diseases (eg, COPD, CF) by disrupting
disulfide bonds. Also used as an antidote for acetaminophen overdose.
Dextromethorphan Antitussive (antagonizes NMDA glutamate receptors). Synthetic codeine analog. Has mild opioid
effect when used in excess. Naloxone can be given for overdose. Mild abuse potential. May cause
serotonin syndrome if combined with other serotonergic agents.
Pseudoephedrine, phenylephrine
mEChANISm α-adrenergic agonists.
ClINICAl USE Reduce hyperemia, edema (used as nasal decongestants); open obstructed eustachian tubes.
ADVERSE EFFECTS Hypertension. Rebound congestion if used more than 4–6 days. Can also cause CNS stimulation/
anxiety (pseudoephedrine).
Pulmonary hypertension drugs
DRUg mEChANISm ClINICAl NOTES
Endothelin receptor Competitively antagonizes endothelin-1 Hepatotoxic (monitor LFTs).
antagonists receptors pulmonary vascular resistance. Example: bosentan.
PDE-5 inhibitors Inhibits PDE-5 cGMP prolonged Also used to treat erectile dysfunction.
vasodilatory effect of NO. Contraindicated when taking nitroglycerin
or other nitrates (due to risk of severe
hypotension).
Example: sildenafil.
Prostacyclin analogs PGI (prostacyclin) with direct vasodilatory Side effects: flushing, jaw pain.
2
effects on pulmonary and systemic arterial Examples: epoprostenol, iloprost.
vascular beds. Inhibits platelet aggregation.
FAS1_2019_16-Respiratory.indd 686 11/8/19 7:34 AM