Page 88 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 88
44 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR
tRNA
Structure 75–90 nucleotides, 2º structure, cloverleaf form, anticodon end is opposite 3′ aminoacyl end. All
tRNAs, both eukaryotic and prokaryotic, have CCA at 3′ end along with a high percentage of
chemically modified bases. The amino acid is covalently bound to the 3′ end of the tRNA. CCA
Can Carry Amino acids.
T-arm: contains the TΨC (ribothymidine, pseudouridine, cytidine) sequence necessary for tRNA-
ribosome binding. T-arm Tethers tRNA molecule to ribosome.
D-arm: contains Dihydrouridine residues necessary for tRNA recognition by the correct aminoacyl-
tRNA synthetase. D-arm allows Detection of the tRNA by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase.
Attachment site: the 5′-CCA-3′ is the amino acid acceptor site.
Charging Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase (uses ATP; 1 unique enzyme per respective amino acid) and
binding of charged tRNA to the codon are responsible for the accuracy of amino acid selection.
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase matches an amino acid to the tRNA by scrutinizing the amino acid
before and after it binds to tRNA. If an incorrect amino acid is attached, the bond is hydrolyzed.
A mischarged tRNA reads the usual codon but inserts the wrong amino acid.
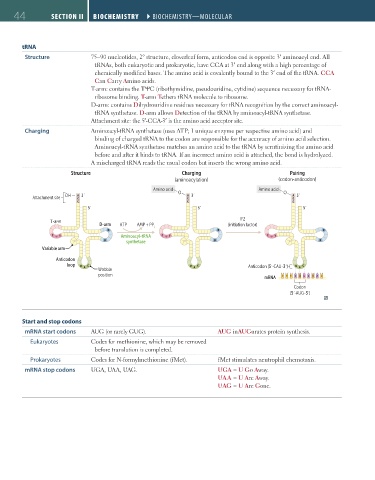
Structure Charging Pairing
(aminoacylation) (codon-anticodon)
Amino acid Amino acid
OH A 3´ O A 3´ O A 3´
Attachment site C C C
C C C
5´ 5´ 5´
IF2
T-arm
D-arm ATP AMP + PP i (initiation factor)
D D D
C T Aminoacyl-tRNA C T C T
Ψ Ψ Ψ
D synthetase D D
Variable arm
Anticodon
loop U A C U A C Anticodon (5´-CAU-3´) U A C
Wobble
position C C C A U G A U A C
mRNA
Codon
(5´-AUG-3´)
Start and stop codons
mRNA start codons AUG (or rarely GUG). AUG inAUGurates protein synthesis.
Eukaryotes Codes for methionine, which may be removed
before translation is completed.
Prokaryotes Codes for N-formylmethionine (fMet). fMet stimulates neutrophil chemotaxis.
mRNA stop codons UGA, UAA, UAG. UGA = U Go Away.
UAA = U Are Away.
UAG = U Are Gone.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 44 11/7/19 3:16 PM