Page 89 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 89
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—MOlECUlAR SECTION II 45
Protein synthesis
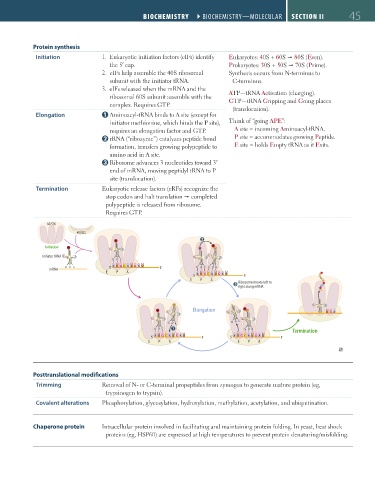
Initiation 1. Eukaryotic initiation factors (eIFs) identify Eukaryotes: 40S + 60S 80S (Even).
the 5′ cap. Prokaryotes: 30S + 50S 70S (Prime).
2. eIFs help assemble the 40S ribosomal Synthesis occurs from N-terminus to
subunit with the initiator tRNA. C-terminus.
3. eIFs released when the mRNA and the
ribosomal 60S subunit assemble with the ATP—tRNA Activation (charging).
complex. Requires GTP. GTP—tRNA Gripping and Going places
(translocation).
Elongation Aminoacyl-tRNA binds to A site (except for
initiator methionine, which binds the P site), Think of “going APE”:
requires an elongation factor and GTP. A site = incoming Aminoacyl-tRNA.
rRNA (“ribozyme”) catalyzes peptide bond P site = accommodates growing Peptide.
formation, transfers growing polypeptide to E site = holds Empty tRNA as it Exits.
amino acid in A site.
Ribosome advances 3 nucleotides toward 3′
end of mRNA, moving peptidyl tRNA to P
site (translocation).
Termination Eukaryotic release factors (eRFs) recognize the
stop codon and halt translation completed
polypeptide is released from ribosome.
Requires GTP.
60/50S
40/30S
R
M
Initiation M M M H
Initiator tRNA
U A C
mRNA U A C 5´ A U G C A U G A U 3´ U A C G U A
E P A
5´ A U G C A U G A U 3´
E P A
S Ribosome moves left to
right along mRNA
H
M Elongation M H U G A
G U A U A C
U A C Q G U A Termination
5´ A U G C A U G A U 3´ 5´ A U G C A U G A U 3´
E P A E P A
Posttranslational modifications
Trimming Removal of N- or C-terminal propeptides from zymogen to generate mature protein (eg,
trypsinogen to trypsin).
Covalent alterations Phosphorylation, glycosylation, hydroxylation, methylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination.
Chaperone protein Intracellular protein involved in facilitating and maintaining protein folding. In yeast, heat shock
proteins (eg, HSP60) are expressed at high temperatures to prevent protein denaturing/misfolding.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 45 11/7/19 3:16 PM