Page 90 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 90
46 SECTION II BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR
` `BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR
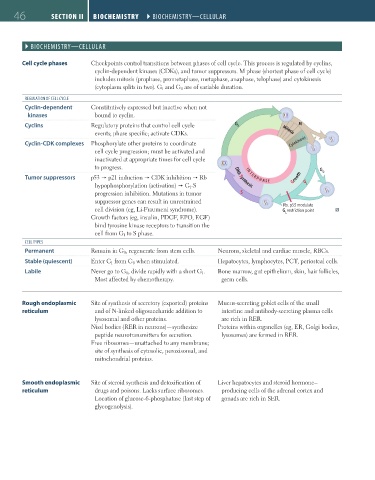
Cell cycle phases Checkpoints control transitions between phases of cell cycle. This process is regulated by cyclins,
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and tumor suppressors. M phase (shortest phase of cell cycle)
includes mitosis (prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase) and cytokinesis
(cytoplasm splits in two). G 1 and G 0 are of variable duration.
REGUlATION OF CEll CYClE
Cyclin-dependent Constitutively expressed but inactive when not
kinases bound to cyclin.
Cyclins Regulatory proteins that control cell cycle G 2 M
events; phase specific; activate CDKs. Mitosis
Cyclin-CDK complexes Phosphorylate other proteins to coordinate Cytokinesis
cell cycle progression; must be activated and
inactivated at appropriate times for cell cycle
to progress. G
Tumor suppressors p53 p21 induction CDK inhibition Rb DNA Synthesis Growth O
I N T E R P H A S E
hypophosphorylation (activation) G 1 -S G 1
progression inhibition. Mutations in tumor S
suppressor genes can result in unrestrained
Rb, p53 modulate
cell division (eg, Li-Fraumeni syndrome). G restriction point
1
Growth factors (eg, insulin, PDGF, EPO, EGF)
bind tyrosine kinase receptors to transition the
cell from G 1 to S phase.
CEll TYPES
Permanent Remain in G 0 , regenerate from stem cells. Neurons, skeletal and cardiac muscle, RBCs.
Stable (quiescent) Enter G 1 from G 0 when stimulated. Hepatocytes, lymphocytes, PCT, periosteal cells.
Labile Never go to G 0 , divide rapidly with a short G 1 . Bone marrow, gut epithelium, skin, hair follicles,
Most affected by chemotherapy. germ cells.
Rough endoplasmic Site of synthesis of secretory (exported) proteins Mucus-secreting goblet cells of the small
reticulum and of N-linked oligosaccharide addition to intestine and antibody-secreting plasma cells
lysosomal and other proteins. are rich in RER.
Nissl bodies (RER in neurons)—synthesize Proteins within organelles (eg, ER, Golgi bodies,
peptide neurotransmitters for secretion. lysosomes) are formed in RER.
Free ribosomes—unattached to any membrane;
site of synthesis of cytosolic, peroxisomal, and
mitochondrial proteins.
Smooth endoplasmic Site of steroid synthesis and detoxification of Liver hepatocytes and steroid hormone–
reticulum drugs and poisons. Lacks surface ribosomes. producing cells of the adrenal cortex and
Location of glucose-6-phosphatase (last step of gonads are rich in SER.
glycogenolysis).
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 46 11/7/19 3:16 PM