Page 91 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 91
BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR BIOCHEmISTRY ``BIOCHEMISTRY—CEllUlAR SECTION II 47
Cell trafficking Golgi is distribution center for proteins and lipids from ER to vesicles and plasma membrane.
Posttranslational events in Golgi include modifying N-oligosaccharides on asparagine, adding
O-oligosaccharides on serine and threonine, and adding mannose-6-phosphate to proteins for
lysosomal trafficking.
Endosomes are sorting centers for material from outside the cell or from the Golgi, sending it to
lysosomes for destruction or back to the membrane/Golgi for further use.
I-cell disease (inclusion cell disease/mucolipidosis type II)—inherited lysosomal storage disorder
(autosomal recessive); defect in N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase failure of the
Golgi to phosphorylate mannose residues ( mannose-6-phosphate) on glycoproteins proteins
are secreted extracellularly rather than delivered to lysosomes. Results in coarse facial features,
gingival hyperplasia, clouded corneas, restricted joint movements, claw hand deformities,
kyphoscoliosis, and high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes. Often fatal in childhood.
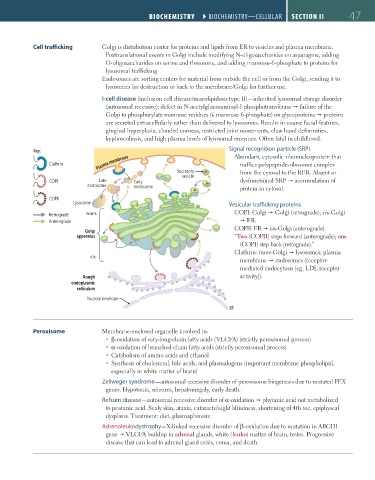
Signal recognition particle (SRP)
Key: Abundant, cytosolic ribonucleoprotein that
Plasma membrane
Clathrin traffics polypeptide-ribosome complex
Secretory from the cytosol to the RER. Absent or
vesicle
COPI Late Early dysfunctional SRP accumulation of
endosome endosome protein in cytosol.
COPII
Lysosome Vesicular trafficking proteins
Retrograde trans COPI: Golgi Golgi (retrograde); cis-Golgi
Anterograde ER.
COPII: ER cis-Golgi (anterograde).
Golgi
apparatus “Two (COPII) steps forward (anterograde); one
(COPI) step back (retrograde).”
Clathrin: trans-Golgi lysosomes; plasma
cis
membrane endosomes (receptor-
mediated endocytosis [eg, LDL receptor
Rough activity]).
endoplasmic
reticulum
Nuclear envelope
Peroxisome Membrane-enclosed organelle involved in:
β-oxidation of very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFA) (strictly peroxisomal process)
α-oxidation of branched-chain fatty acids (strictly peroxisomal process)
Catabolism of amino acids and ethanol
Synthesis of cholesterol, bile acids, and plasmalogens (important membrane phospholipid,
especially in white matter of brain)
Zellweger syndrome—autosomal recessive disorder of peroxisome biogenesis due to mutated PEX
genes. Hypotonia, seizures, hepatomegaly, early death.
Refsum disease—autosomal recessive disorder of α-oxidation phytanic acid not metabolized
to pristanic acid. Scaly skin, ataxia, cataracts/night blindness, shortening of 4th toe, epiphyseal
dysplasia. Treatment: diet, plasmapheresis.
Adrenoleukodystrophy—X-linked recessive disorder of β-oxidation due to mutation in ABCD1
gene VLCFA buildup in adrenal glands, white (leuko) matter of brain, testes. Progressive
disease that can lead to adrenal gland crisis, coma, and death.
FAS1_2019_01-Biochem.indd 47 11/7/19 3:16 PM