Page 168 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 168
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
When rusting occurs, the metal atoms are exposed to an environment containing
KEY POINT
water molecules. Here, they give up electrons and become positively charged ions.
The electrochemical
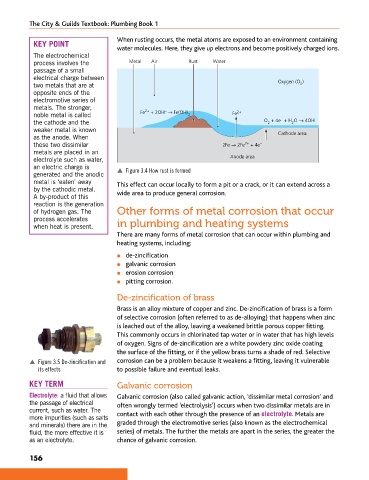
process involves the Metal Air Rust Water
passage of a small
electrical charge between
two metals that are at Oxygen (O 2 )
opposite ends of the
electromotive series of
metals. The stronger, 2+ −
noble metal is called Fe + 2OH → Fe(OH) 2 Fe 2+
−
the cathode and the O + 4e + H O → 4OH −
2
2
weaker metal is known
as the anode. When Cathode area
these two dissimilar 2Fe → 2Fe + 4e −
2+
metals are placed in an
electrolyte such as water, Anode area
an electric charge is p Figure 3.4 How rust is formed
generated and the anodic
metal is ‘eaten’ away This effect can occur locally to form a pit or a crack, or it can extend across a
by the cathodic metal. wide area to produce general corrosion.
A by-product of this
reaction is the generation
of hydrogen gas. The Other forms of metal corrosion that occur
process accelerates
when heat is present. in plumbing and heating systems
There are many forms of metal corrosion that can occur within plumbing and
heating systems, including:
● de-zincification
l galvanic corrosion
l erosion corrosion
l pitting corrosion.
De-zincification of brass
Brass is an alloy mixture of copper and zinc. De-zincification of brass is a form
of selective corrosion (often referred to as de-alloying) that happens when zinc
is leached out of the alloy, leaving a weakened brittle porous copper fitting.
This commonly occurs in chlorinated tap water or in water that has high levels
of oxygen. Signs of de-zincification are a white powdery zinc oxide coating
the surface of the fitting, or if the yellow brass turns a shade of red. Selective
p Figure 3.5 De-zincification and corrosion can be a problem because it weakens a fitting, leaving it vulnerable
its effects to possible failure and eventual leaks.
KEY TERM Galvanic corrosion
Electrolyte: a fluid that allows Galvanic corrosion (also called galvanic action, ‘dissimilar metal corrosion’ and
the passage of electrical often wrongly termed ‘electrolysis’) occurs when two dissimilar metals are in
current, such as water. The contact with each other through the presence of an electrolyte. Metals are
more impurities (such as salts
and minerals) there are in the graded through the electromotive series (also known as the electrochemical
fluid, the more effective it is series) of metals. The further the metals are apart in the series, the greater the
as an electrolyte. chance of galvanic corrosion.
156
9781510416482.indb 156 29/03/19 8:55 PM