Page 196 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 196
The City & Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1
Resistance ohm R or Ω Unit of DC resistance
R = V ÷ I
Conductance siemen G Reciprocal of resistance
G = 1 ÷ R
Capacitance farad C Unit of capacitance
C = Q ÷ V
Charge coulomb Q Unit of electrical charge
Q = C × V
Power watts W Unit of power
P = V × I
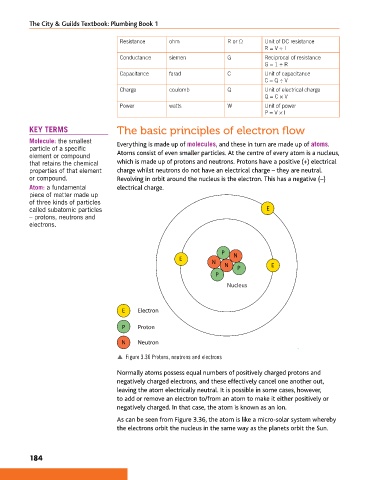
KEY TERMS The basic principles of electron flow
Molecule: the smallest Everything is made up of molecules, and these in turn are made up of atoms.
particle of a specific
element or compound Atoms consist of even smaller particles. At the centre of every atom is a nucleus,
that retains the chemical which is made up of protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive (+) electrical
properties of that element charge whilst neutrons do not have an electrical charge – they are neutral.
or compound. Revolving in orbit around the nucleus is the electron. This has a negative (−)
Atom: a fundamental electrical charge.
piece of matter made up
of three kinds of particles
called subatomic particles E
– protons, neutrons and
electrons.
P
E N
N
N E
P
P
Nucleus
E Electron
P Proton
N Neutron
.
p Figure 3.36 Protons, neutrons and electrons
Normally atoms possess equal numbers of positively charged protons and
negatively charged electrons, and these effectively cancel one another out,
leaving the atom electrically neutral. It is possible in some cases, however,
to add or remove an electron to/from an atom to make it either positively or
negatively charged. In that case, the atom is known as an ion.
As can be seen from Figure 3.36, the atom is like a micro-solar system whereby
the electrons orbit the nucleus in the same way as the planets orbit the Sun.
184
9781510416482.indb 184 29/03/19 8:55 PM