Page 430 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 430
396 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
(.045 CFR DISPL.)
250
200
6T'
12 150
10 100
B
50
5
2 0
AIRFLOW BASED UPON "Hg VAC
�,so INLET: 70" F 2
::. t+H,..........., DISCHARGE: 29.92" Hg Abs. 5
Li.
S12s B
1- 10
w 12
...J 100
�CFM 15
�75
�
g 50 8
Li. "H VAC.
0:: 15
< 25 7
12
0 6
10
5
B
4
5 BHP
3
2
0::
� 2
0
0..
w
(/)
0::
0
:r: 0
1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
RPM
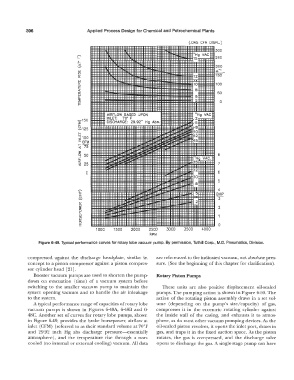
Figure 6-49. Typical performance curves for rotary lobe vacuum pump. By permission, Tuthill Corp., M.D. Pneumatics, Division.
compressed against the discharge headplate, similar in are referenced to the indicated vacuum, not absolute pres-
concept to a piston compressor against a piston compres- sure. (See the beginning of this chapter for clarification).
sor cylinder head [21].
Booster vacuum pumps are used to shorten the pump- Rotary Piston Pumps
down on evacuation (time) of a vacuum system before
switching to the smaller vacuum pump to maintain the These units are also positive displacement oil-sealed
system opening vacuum and to handle the air inleakage pumps. The pumping action is shown in Figure 6--50. The
to the system. action of the rotating piston assembly draws in a set vol-
A typical performance range of capacities of rotary lobe ume (depending on the pump's size/capacity) of gas,
vacuum pumps is shown in Figures 6-48A, 6-48B and 6- compresses it in the eccentric rotating cylinder against
48C. Another set of curves for rotary lobe pumps, shown the inside wall of the casing, and exhausts it to atmos-
in Figure 6-49, provides the brake horsepower, airflow at phere, as do most other vacuum pumping devices. AE. the
inlet (CFM) (referred to as their standard volume at 70°F oil-sealed piston revolves, it opens the inlet port, draws in
and 29.92 inch Hg abs discharge pressure-essentially gas, and traps it in the fixed suction space. As the piston
atmosphere), and the temperature rise through a non- rotates, the gas is compressed, and the discharge valve
cooled (no internal or external cooling) vacuum. All data opens to discharge the gas. A single-stage pump can have