Page 492 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 492
458 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Stamped Burst Pressure At Coincident Temperature
160
Method 2
150 PSI Q1 72 F
150
EXAMPLE
2" PREBULGED ALU,\41NUM
RUPTURE DISC BURST PRESSURE
150 PSI �1 n- F
DETERMINE BURST PRESSURE AT
210 F
"0
130
123 PSI. f1 240 F
120
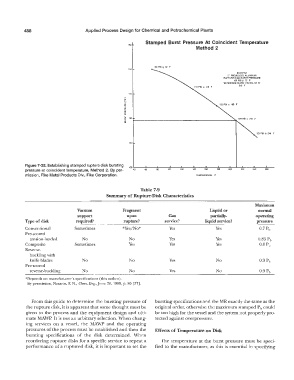
Figure 7-32. Establishing stamped rupture disk bursting
pressure at coincident temperature, Method 2. By per-
mission, Fike Metal Products Div., Fike Corporation. TEMPERATURE. F
Table 7-9
Summary of Rupture-Disk Characteristics
Maximum
Vacuum Fragment Liquid or normal
support upon Gas partially- operating
Type of disk required? rupture? service? liquid service? pressure
Conventional Sometimes *Yes/No* Yes Yes 0.7 Pb
Pre-scored
tension-loaded No No Yes Yes 0.85 Pb
Composite Sometimes Yes Yes Yes 0.8 Pb
Reverse-
buckling with
knife blades No No Yes No 0.9 Pb
Pre-scored
reverse-buckling No No Yes No 0.9 Pb
*Depends on manufacturer's specifications ( this author).
By permission, Nazario, F. N., Chem. Eng., June 20, l 988, p. 86 [37].
From this guide to determine the bursting pressure of bursting specifications and the MR exactly the same as the
the rupture disk, it is apparent that some thought must be original order, otherwise the maximum stamped Pb could
given to the process and the equipment design and ulti- be too high for the vessel and the system not properly pro-
mate MAWP. It is not an arbitrary selection. When chang- tected against overpressure.
ing services on a vessel, the MAWP and the operating
pressures of the process must be established and then the Effects of Temperature on Disk
bursting specifications of the disk determined. \,Vhen
reordering rupture disks for a specific service lo repeat a The temperature at the burst pressure must be speci-
performance of a ruptured disk, it is important to set the fied to the manufacturer, as this is essential in specifying