Page 551 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 551
Applied Process Design 517
Vent Release Pressure Maximum Pressure During Venting
P,ed � 0.2 bar ga ---... �
�I\: P,ed = 0.4 bar ga ---.,_ r-, i,..,""
'� � �pstat=0.1 bar ga P,ed = 0.6 bar ga � � � '',/ .... � �
I\:
�' v P,ed = 0.8 bar ga , ,--..;;.. ' �I\ ,I � � �I,' ,,..
... ��
i.,-- Pstat = 0 .2 bar ga
P,ed = 1.0 bar ga - rs..
'�'\. ,I v V,, i,-- P,tat = 0 .5 bar ga P,ed = 1.5 bar ga ------ � � i'\ " ... � �,/� � � �v
i"\
'\.� 1/11 I/ ,I v P,ed = 2.0 bar ga � r- I'\ " � � i.,,
1,1'
' �i,."'v "\ ' � �
I(
� � 'rt'� �.I7
/ ....
1
"� � / h � �� )
'� � VA � �:....
� ' ... i. � �
�'\. ..... � h� V/
....
� l/ � �::::��
�
' �l'I � � � � 1,.,1
� l' � � t-
�,,
l'I i'I '- v
l'I.. � �
� � �
� �
� I
""'
!;0 10 0.1 10 100 1000
------Vent Area, m 2 Vessel Volume, m 3----- �
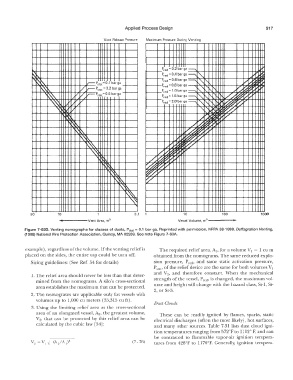
Figure 7-650. Venting nomographs for classes of dusts, Pstat = 0.1 bar ga. Reprinted with permission, NFPA 68-1988, Deflagration Venting,
(1988) National Fire Protection Association, Quincy, MA 02269. See note Figure 7-63A.
example), regardless of the volume. If the venting relief is The required relief area, A 1, for a volume \1 1 = 1 cum
placed on the sides, the entire top could be torn off. obtained from the nomograms. The same reduced explo-
Sizing guidelines: (See Ref. 54 for details) sion pressure, Pred, and same static activation pressure,
Ps,at• of the relief device are the same for both volumes V 1
and V 2, and therefore constant. When the mechanical
l. The relief area should never be less than that deter-
mined from the nomograms. A silo's cross-sectional strength of the vessel, Pred• is changed, the maximum vol-
ume and height will change with the hazard class, St-1, St-
area establishes the maximum that can be protected.
2, or St-3.
2. The nomograms are applicable only for vessels with
volumes up to 1,000 cu meters (35,315 cu ft).
Dust Clouds
3. Using the limiting relief area as the cross-sectional
area of an elongated vessel, A 2, the greatest volume, These can be readily ignited by flames, sparks, static
V2, that can be protected by this relief area can be electrical discharges ( often the most likely), hot surfaces,
calculated by .. he cubic law [54]: and many other sources. Table 7-31 lists dust cloud igni-
tion temperatures ranging from 572°F to 1112° F, and can
be contrasted to flammable vapor-air ignition tempera-
(7- 76) tures from 428°F to 1170°F. Generally, ignition tempera-