Page 550 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 550
516 Applied Process Design for Chemical and Petrochemical Plants
Maximum Pressure During Venting
111 I
·-- 111 I I I
II
I\. Ks 1 ,_bar·m/sec.
'
� r,.. ' v-- 50 P,ed• bar ga
/ v-- 75
I\.
0.6
� "' ' '\ / / ,-- 100 0.8 ,,
...
I'\.
r\ ' ' ' ,, / / / �150 1.0--..,_ ,,
r\ ' ' ' / I/ / / -200 <,
,,
,,
''
'\
/
1.3 ------
" �,, ' ,, / �v / / 250 2.0- '\ ' ' ,,. �
"'
vv
�I\. .,
'
<,
1.6-
'
300
I{ V/ //
400
.. ,
''
"'
r-,
'l�,
I\. '
-500
"'
-,
I\.'-
"
"-1'- '
/,
)<1/ )( /
I\.''\
,,.
IX/ v
�,,,
I� � x>, v )j / ./ -600 " '\ ' ,, ,,, [..., .,, ;
r-,
' "
,,..,
I/ 0
...
'
r\.-
'-X //
'
""'' ')c ,, ' ' � � / //
I\.
�
� '/. /
vr'\
I; � v
' I'- '\
I,
''
'' ' ,; ,; ,, i;'L; ....,
'/'Y"'
,I\.
:,['\
,;
�-' ' ''\ I\. I\. /,; . ...., //1,
"'
,; "/ / /
"'
I'\. '
�
,,,
I\.'-
... �'\ I\..,, � I\. I\. "'// »: ,:..
.,,
I� �,, ' -, ,;"'.,, V/
//
///
I\.
� I\.
'
""'' "� ,, ' ' / // ,; ..... .... .,, //
I\.
' '
I/ L;'c,
�
/
;' .... 1,;
' ' '
� ' '' ' // ,,,,;r,,;
�"'' �, ,, ,, // ,, / v
' ''
,, /,, '/
... �, '' c>
�, ,,,
-i ... , ' '' "//
... �,,
""''
�' ...
100 10 0.1 10 100 1000
Vent Area, m 2 Vessel Volume, m 3
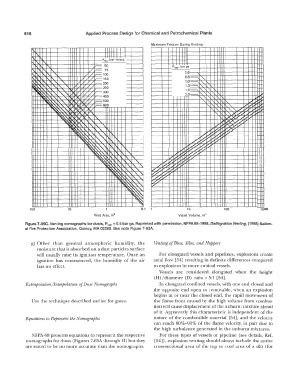
Figure 7-65C. Venting nomographs for dusts, Psiai = 0.5 bar ga. Reprinted with permission, NFPA 68-1988, Def/agration Venting, (1988) Nation-
al Fire Protection Association, Quincy, MA 02269. See note Figure 7-63A.
g) Other than general atmospheric humidity, the Venting of Bins, Silos, and Hoppers
moisture that is absorbed on a dust particles surface
will usually raise its ignition temperature. Once an For elongated vessels and pipelines, explosions create
ignition has commenced, the humidity of the air axial flow [54) resulting in definite differences compared
has no effect. to explosions in more cubical vessels.
Vessels are considered elongated when the height
(H)/diameter (D) ratio> 5:1 l54].
Extrapolation/Interpolation ofDust Nomographs In elongated confined vessels, with one end closed and
the opposite end open or removable, when an explosion
begins at or near the closed end, the rapid movement of
Use the technique described earlier for gases. the flame front caused by the high volume from combus-
tion will cause displacement of the unburnt mixture ahead
of it. Apparently this characteristic is independent of the
Equations to Represent the Nomographs nature of the combustible material [54], and the velocity
can reach 80%-90% of the flame velocity, in part due to
the high turbulence generated in the unburnt mixtures.
NFPA-68 presents equations to represent the respective For these types of vessels or pipeline (see details, Ref.
nomographs for dusts (Figures 7-65A through H) but they [54]), explosion venting should always include the entire
are slated to be no more accurate than the nomographs. cross-sectional area of the top or roof area of a silo (for