Page 9 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 9
Form
4
Chapter 5 Chemical Bond Chemistry
5.1 Basics of Compound Formation
1. Different elements that are chemically bonded Types of Chemical Bonds
together but not mixed together are called http://bit.ly/2OeUnAH
compounds.
Example:
• Water is a compound of hydrogen and oxygen 5. Chemical bonds are formed through the transfer
• Carbon dioxide is a compound of carbon and of electrons or share of electrons.
oxygen (a) During the transfer of electrons, a metal atom
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
• Rust is a compound of iron, oxygen and with one, two or three valence electrons will
hydrogen donate its valence electrons whereas a non-
2. Atoms form chemical bond to achieve a stable metal atom with five, six or seven valence
electron arrangement. electrons will receive the electrons.
3. Noble gases exist as monoatomic gases and Example:
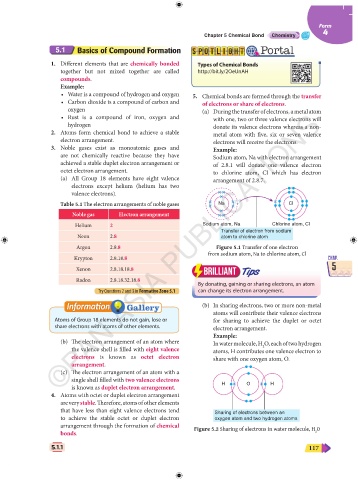
are not chemically reactive because they have Sodium atom, Na with electron arrangement
achieved a stable duplet electron arrangement or of 2.8.1 will donate one valence electron
octet electron arrangement. to chlorine atom, Cl which has electron
(a) All Group 18 elements have eight valence arrangement of 2.8.7.
electrons except helium (helium has two
valence electrons).
Table 5.1 The electron arrangements of noble gases Na Cl
Noble gas Electron arrangement
Helium 2 Sodium atom, Na Chlorine atom, Cl
Transfer of electron from sodium
Neon 2.8 atom to chlorine atom
Argon 2.8.8 Figure 5.1 Transfer of one electron
from sodium atom, Na to chlorine atom, Cl
CHAP. Krypton 2.8.18.8 CHAP.
5 Xenon 2.8.18.18.8 5
Radon 2.8.18.32.18.8
By donating, gaining or sharing electrons, an atom
Try Questions 2 and 3 in Formative Zone 5.1 can change its electron arrangement.
(b) In sharing electrons, two or more non-metal
atoms will contribute their valence electrons
Atoms of Group 18 elements do not gain, lose or for sharing to achieve the duplet or octet
share electrons with atoms of other elements. electron arrangement.
Example:
(b) The electron arrangement of an atom where In water molecule, H O, each of two hydrogen
2
the valence shell is filled with eight valence atoms, H contributes one valence electron to
electrons is known as octet electron share with one oxygen atom, O.
arrangement.
(c) The electron arrangement of an atom with a
single shell filled with two valence electrons
is known as duplet electron arrangement. H O H
4. Atoms with octet or duplet electron arrangement
are very stable. Therefore, atoms of other elements
that have less than eight valence electrons tend Sharing of electrons between an
to achieve the stable octet or duplet electron oxygen atom and two hydrogen atoms
arrangement through the formation of chemical Figure 5.2 Sharing of electrons in water molecule, H O
bonds. 2
5.1.1 117