Page 12 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 12
Form
4
Chemistry Chapter 5 Chemical Bond
Effect of Hydrogen Bond on the Physical
Properties of Substances
1. Hydrogen bonds will affect the solubility and The oxygen atom is partially negatively charged,
boiling point of a covalent compound. and the hydrogen atom is partially positively
2. Boiling point: charged.
(a) The boiling point of ethane, C H is
2
6
–89 °C, whereas the boiling point of ethanol, 4. Covalent compounds such as ammonia, NH
3
and hydrogen fluoride, HF also can form
C H OH is 78 °C. hydrogen bonds with water molecules, H O.
2
5
(b) Molecules of ethane, C H are attracted by This explains why ammonia, NH and hydrogen
2
5©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
2
6
weak Van der Waals attraction forces only. fluoride, HF can dissolve in water, H O and has
3
2
Molecules of ethanol, C H OH are attracted higher boiling point compared to other covalent
2
5
by weak Van der Waals attraction forces and compounds.
hydrogen bonds.
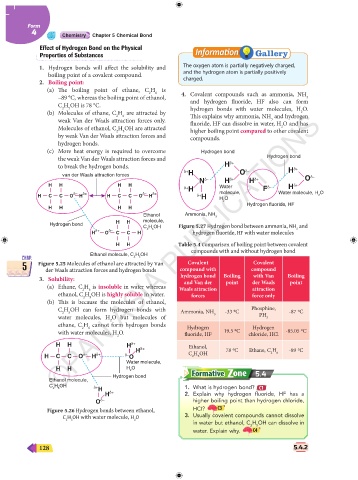
(c) More heat energy is required to overcome Hydrogen bond
the weak Van der Waals attraction forces and Hydrogen bond
to break the hydrogen bonds. H δ+ δ+
δ+ H O δ– H
van der Waals attraction forces δ–
N δ– H δ+ H δ+ O
H H H H δ+
δ+ H Water F δ– H
δ– δ+ δ– δ+ molecule, Water molecule, H O
H C C O H H C C O H δ+ H H O 2
2
Hydrogen fluoride, HF
H H H H
Ethanol Ammonia, NH 3
H H molecule,
Hydrogen bond Figure 5.27 Hydrogen bond between ammonia, NH and
C H OH
δ+ δ– 2 5 3
H O C C H hydrogen fluoride, HF with water molecules
H H Table 5.4 Comparison of boiling point between covalent
compounds with and without hydrogen bond
Ethanol molecule, C H OH
CHAP. 2 5 Covalent Covalent CHAP.
5 Figure 5.25 Molecules of ethanol are attracted by Van compound with compound 5
der Waals attraction forces and hydrogen bonds
with Van
3. Solubility: hydrogen bond Boiling der Waals Boiling
and Van der
point
point
(a) Ethane, C H is insoluble in water whereas Waals attraction attraction
6
2
ethanol, C H OH is highly soluble in water. forces force only
2
5
(b) This is because the molecules of ethanol,
C H OH can form hydrogen bonds with Ammonia, NH -33 0C Phosphine, -87 0C
2
5
water molecules, H O but molecules of 3 PH 3
2
ethane, C H cannot form hydrogen bonds Hydrogen Hydrogen
2
6
with water molecules, H O. fluoride, HF 19.5 0C chloride, HCl -85.05 0C
2
H H H δ+ Ethanol,
H δ+ 78 0C Ethane, C H 6 -89 0C
2
δ– δ+ δ– C H OH
H C C O H O 2 5
Water molecule,
H H H O
2
Hydrogen bond 5.4
Ethanol molecule,
C H OH 1. What is hydrogen bond? C1
H δ+
2 δ+
H 2. Explain why hydrogen fluoride, HF has a
O δ– higher boiling point than hydrogen chloride,
Figure 5.26 Hydrogen bonds between ethanol, HCI? C3
C H OH with water molecule, H O 3. Usually covalent compounds cannot dissolve
2
5
2
in water but ethanol, C H OH can dissolve in
2 5
water. Explain why. C4
128 5.4.2