Page 11 - Spotlight A+ Form 4 & 5 Chemistry KSSM
P. 11
Form
4
Chapter 5 Chemical Bond Chemistry
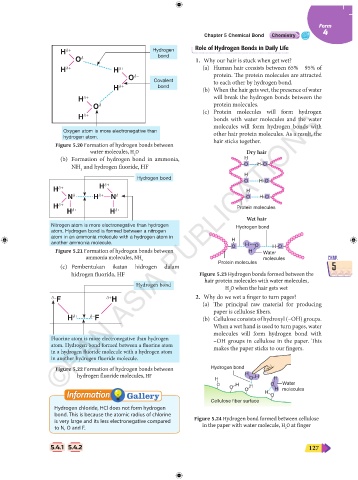
Role of Hydrogen Bonds in Daily Life
H δ+ Hydrogen
O δ– bond 1. Why our hair is stuck when get wet?
H δ+ H δ+ (a) Human hair consists between 65% – 95% of
O δ– protein. The protein molecules are attracted
Covalent to each other by hydrogen bond.
H δ+ bond (b) When the hair gets wet, the presence of water
H δ+ will break the hydrogen bonds between the
protein molecules.
O δ– (c) Protein molecules will form hydrogen
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
H δ+ bonds with water molecules and the water
molecules will form hydrogen bonds with
Oxygen atom is more electronegative than other hair protein molecules. As a result, the
hydrogen atom.
Figure 5.20 Formation of hydrogen bonds between hair sticks together.
water molecules, H O Dry hair
2
(b) Formation of hydrogen bond in ammonia, H
NH and hydrogen fluoride, HF O H O
3
H
Hydrogen bond
O H O
H δ+ H δ+ H
N δ– H δ+ N δ– O H O
H δ+ Protein molecules
H δ+ H δ+
Wet hair
Nitrogen atom is more electronegative than hydrogen Hydrogen bond
atom. Hydrogen bond is formed between a nitrogen
atom in an ammonia molecule with a hydrogen atom in H
another ammonia molecule. H O
H O
Figure 5.21 Formation of hydrogen bonds between O H Water
CHAP. ammonia molecules, NH 3 molecules CHAP.
5 (c) Pembentukan ikatan hidrogen dalam Protein molecules 5
hidrogen fluorida, HF Figure 5.23 Hydrogen bonds formed between the
hair protein molecules with water molecules,
Hydrogen bond H O when the hair gets wet
2
δ– F δ+ H 2. Why do we wet a finger to turn pages?
(a) The principal raw material for producing
paper is cellulose fibers.
H δ+ δ– F (b) Cellulose consists of hydroxyl (–OH) groups.
When a wet hand is used to turn pages, water
molecules will form hydrogen bond with
Fluorine atom is more electronegative than hydrogen –OH groups in cellulose in the paper. This
atom. Hydrogen bond formed between a fluorine atom
in a hydrogen fluoride molecule with a hydrogen atom makes the paper sticks to our fingers.
in another hydrogen fluoride molecule.
Figure 5.22 Formation of hydrogen bonds between Hydrogen bond
hydrogen fluoride molecules, HF H H
H O H
O H H O Water
O
O H molecules
H
O
Cellulose fiber surface
Hydrogen chloride, HCl does not form hydrogen
bond. This is because the atomic radius of chlorine
is very large and its less electronegative compared Figure 5.24 Hydrogen bond formed between cellulose
to N, O and F. in the paper with water molecule, H O at finger
2
5.4.1 5.4.2 127