Page 13 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 5 KSSM
P. 13
PAPER 2
Section A
Answer all questions.
3
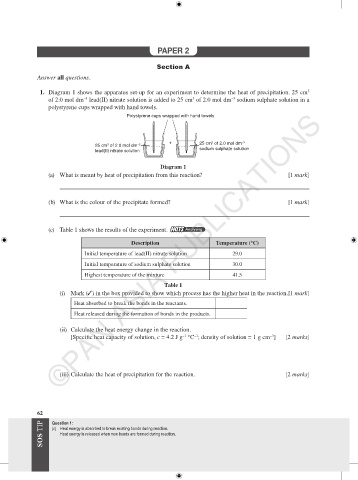
1. Diagram 1 shows the apparatus set-up for an experiment to determine the heat of precipitation. 25 cm
−3
3
−3
of 2.0 mol dm lead(II) nitrate solution is added to 25 cm of 2.0 mol dm sodium sulphate solution in a
polystyrene cups wrapped with hand towels.
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Polystyrene cups wrapped with hand towels
3
−3
+ 25 cm of 2.0 mol dm
3
−3
25 cm of 2.0 mol dm
lead(II) nitrate solution sodium sulphate solution
Diagram 1
(a) What is meant by heat of precipitation from this reaction? [1 mark]
(b) What is the colour of the precipitate formed? [1 mark]
(c) Table 1 shows the results of the experiment. HOTS Analysing
Description Temperature (°C)
Initial temperature of lead(II) nitrate solution 29.0
Initial temperature of sodium sulphate solution 30.0
Highest temperature of the mixture 41.5
Table 1
(i) Mark (3) in the box provided to show which process has the higher heat in the reaction. [1 mark]
Heat absorbed to break the bonds in the reactants.
Heat released during the formation of bonds in the products.
(ii) Calculate the heat energy change in the reaction.
−1
−3
−1
[Specific heat capacity of solution, c = 4.2 J g °C ; density of solution = 1 g cm ] [2 marks]
(iii) Calculate the heat of precipitation for the reaction. [2 marks]
62 Question 1:
SOS TIP (c) Heat energy is absorbed to break existing bonds during reaction.
Heat energy is released when new bonds are formed during reaction.