Page 11 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 5 KSSM
P. 11
3
Chapter Thermochemistry
NOTES
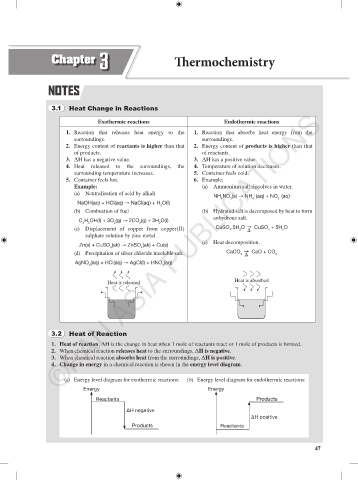
3.1 Heat Change in Reactions
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Exothermic reactions Endothermic reactions
1. Reaction that releases heat energy to the 1. Reaction that absorbs heat energy from the
surroundings. surroundings.
2. Energy content of reactants is higher than that 2. Energy content of products is higher than that
of products. of reactants.
3. ΔH has a negative value. 3. ΔH has a positive value.
4. Heat released to the surroundings, the 4. Temperature of solution decreases.
surrounding temperature increases. 5. Container feels cold.
5. Container feels hot. 6. Example:
Example: (a) Ammonium salt dissolves in water.
(a) Neutralisation of acid by alkali
NH NO (s) → NH (aq) + NO (aq)
−
+
4 3 4 3
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H O(l)
2
(b) Combustion of fuel (b) Hydrated salt is decomposed by heat to form
anhydrous salt.
C H OH(l) + 3O (g) → 2CO (g) + 3H O(l)
2 5 2 2 2
(c) Displacement of copper from copper(II) CuSO .5H O → CuSO + 5H O
4
4
2
2
sulphate solution by zinc metal.
(c) Heat decomposition.
Zn(s) + CuSO (ak) → ZnSO (ak) + Cu(s)
4 4
(d) Precipitation of silver chloride insoluble salt. CaCO → CaO + CO 2
3
AgNO (aq) + HCl(aq) → AgCl(l) + HNO (aq)
3 3
Heat is absorbed
Heat is released
3.2 Heat of Reaction
1. Heat of reaction, ΔH is the change in heat when 1 mole of reactants react or 1 mole of products is formed.
2. When chemical reaction releases heat to the surroundings, ΔH is negative.
3. When chemical reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings, ΔH is positive.
4. Change in energy in a chemical reaction is shown in the energy level diagram.
(a) Energy level diagram for exothermic reactions: (b) Energy level diagram for endothermic reactions:
Energy Energy
Reactants Products
ΔH negative
ΔH positive
Products Reactants
47