Page 7 - 1202 Question Bank Chemistry Form 5 KSSM
P. 7
(d) Three observations may be observed during a 5. The standard cell potential can be obtained based on
displacement reaction of a metal. the following equation.
• The more reactive metal dissolves
• The less reactive metal is deposited E 0 cell = E 0 cathode − E 0 anode
• The colour of the salt solution may change
0
6. The electrode potential value, E is used to predict:
9. Displacement of halogen from its halide solution (a) Substance that undergoes oxidation or reduction.
(a) Halogens are oxidising agents. Conversely, (b) Substance that acts as an oxidising or reducing
halide ions are reducing agents. agent.
(b) A halogen molecule, X , gains electrons to form
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
2 (c) Strength of oxidising or reducing agents.
−
−
the halide ion, X : X (aq) + 2e → 2X (aq)
−
2 Example:
(c) Reactivity or oxidising power of the halogens
decreases going down Group 17. F + 2e 2F − E = +2.87 V
0
−
(d) The halide ion gains electrons to form the 2
−
−
halogen molecule, X : 2X (aq) + 2e → X (aq)
0
−
2 2 Oxidising CI + 2e 2CI − E = +1.36 V
(e) Reducing power of the halide ions increases agent 2
moving down Group 17.
Br + 2e 2Br − E = +1.07 V
0
−
2
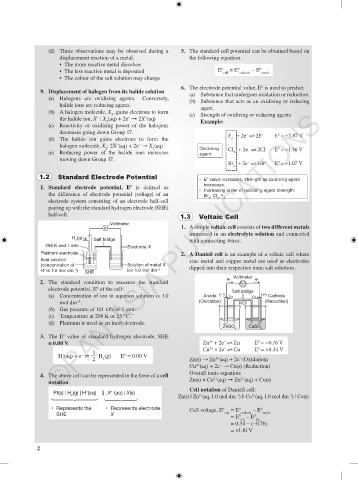
1.2 Standard Electrode Potential
• E° value increases, strength as oxidising agent
0
1. Standard electrode potential, E is defined as increases.
• Increasing order of oxidising agent strength:
the difference of electrode potential (voltage) of an Br , Cl , F
2 2 2
electrode system consisting of an electrode half-cell
pairing up with the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE)
half-cell. 1.3 Voltaic Cell
Voltmeter
V 1. A simple voltaic cell consists of two different metals
immersed in an electrolyte solution and connected
H (g)
2 Salt bridge with connecting wires.
298 K and 1 atm Electrode X
Platinum electrode 2. A Daniell cell is an example of a voltaic cell where
Acid solution zinc metal and copper metal are used as electrodes
(concentration of Solution of metal X dipped into their respective ionic salt solutions.
H is 1.0 mol dm ) SHE ion 1.0 mol dm –3
+
–3
Voltmeter
e – e –
2. The standard condition to measure the standard
0
electrode potential, E of the cell: Salt bridge
(a) Concentration of ion in aqueous solution is 1.0 Anode (–) Zn Cu (+) Cathode
−3
mol dm . (Oxidation) KCl (Reduction)
(b) Gas pressure of 101 kPa or 1 atm.
(c) Temperature at 298 K or 25 °C.
(d) Platinum is used as an inert electrode.
ZnSO CuSO
4 4
0
3. The E value of standard hydrogen electrode, SHE
2+
0
−
= 0.00 V. Zn + 2e Zn E = −0.76 V
Cu + 2e Cu E = +0.34 V
2+
0
−
1
0
–
H (aq) + e ⇌ H (g) E = 0.00 V
+
2+
2 2 Zn(s) → Zn (aq) + 2e (Oxidation)
−
2+
−
Cu (aq) + 2e → Cu(s) (Reduction)
Overall ionic equation:
4. The above cell can be represented in the form of a cell 2+ 2+
notation. Zn(s) + Cu (aq) → Zn (aq) + Cu(s)
Cell notation of Daniell cell:
n+
Pt(s) | H (g) | H (aq) || X (aq) | X(s)
+
2+
2+
−3
−3
2 Zn(s) | Zn (aq, 1.0 mol dm ) || Cu (aq, 1.0 mol dm ) | Cu(s)
⎧ ⎪ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎪ ⎩ ⎧ ⎪ ⎨ ⎪ ⎩
• Represents the • Represents electrode Cell voltage, E 0 = E 0 − E 0
SHE X cell 0 cathode 0 anode
= E − E
Cu Zn
= 0.34 − (−0.76)
= +1.10 V
2