Page 123 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 123
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts] 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
To summarize: The vector ( V ) in a 3D space as shown in [Fig 1.19] can be resolved along
the ‘x’, ‘y’ and ‘z’ axes.
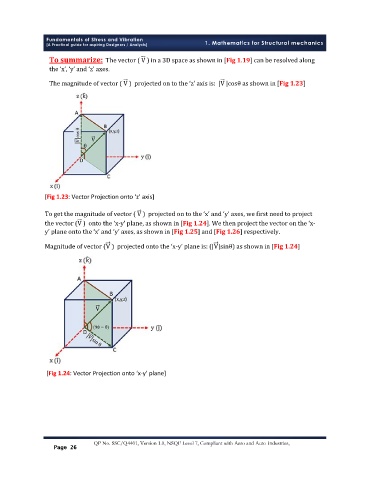
The magnitude of vector ( V ) projected on to the ‘z’ axis is: |V |cosθ as shown in [Fig 1.23]
[Fig 1.23: Vector Projection onto ‘z’ axis]
To get the magnitude of vector ( V ) projected on to the ‘x’ and ‘y’ axes, we first need to project
the vector (V ) onto the ‘x-y’ plane, as shown in [Fig 1.24]. We then project the vector on the ‘x-
y’ plane onto the ‘x’ and ‘y’ axes, as shown in [Fig 1.25] and [Fig 1.26] respectively.
Magnitude of vector (V ) projected onto the ‘x-y’ plane is: (|V|sinθ) as shown in [Fig 1.24]
[Fig 1.24: Vector Projection onto ‘x-y’ plane]
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries,
Page 26