Page 122 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 122
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts]
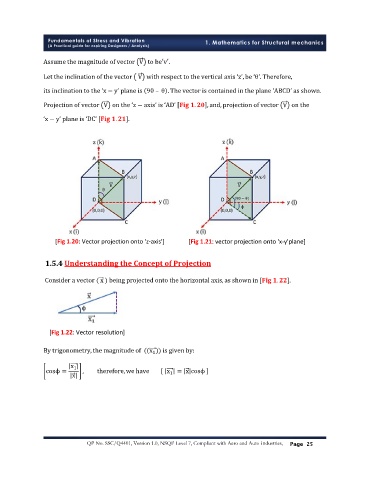
Assume the magnitude of vector V to be′v′.
Let the inclination of the vector V with respect to the vertical axis ‘z’, be ‘θ’. Therefore,
its inclination to the ‘x − y’ plane is 90 – θ . The vector is contained in the plane ‘ABCD’ as shown.
Projection of vector V on the ‘z − axis’ is ‘AD’ . , and, projection of vector V on the
‘x − y’ plane is ‘DC’ [ . ].
[Fig 1.20: Vector projection onto 'z-axis'] [Fig 1.21: vector projection onto 'x-y'plane]
ͳǤͷǤͶ
Consider a vector ( x ) being projected onto the horizontal axis, as shown in [ . ].
[Fig 1.22: Vector resolution]
By trigonometry, the magnitude of ((x )) is given by:
1
x
cosϕ = 1 , therefore, we have x = x cosϕ
x 1
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries, Page 25