Page 168 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 168
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration 1. Mathematics for Structural mechanics
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts]
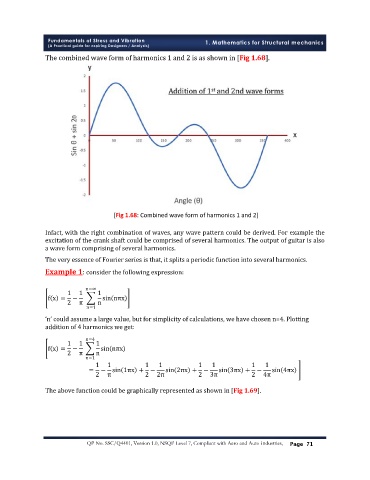
ͳ ʹ ȏ ͳǤͺȐǤ
[Fig 1.68: Combined wave form of harmonics 1 and 2]
ǡ
ǡ
Ǥ
Ǥ
Ǥ
ǡ
Ǥ
ͳǣ
ǣ
n=∞
1 1 1
f x = − sin nπx
2 π n
n=1
‘n’ could assume a large value, but for simplicity of calculations, we have chosen n=4. Plotting
addition of 4 harmonics we get:
n=4
1 1 1
f x = − sin nπx
2 π n
n=1
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
= − sin 1πx + − sin 2πx + − sin 3πx + − sin 4πx
2 π 2 2π 2 3π 2 4π
The above function could be graphically represented as shown in [Fig 1.69].
QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries, Page 71