Page 13 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 13
7.2 Work for a Variable Force 213
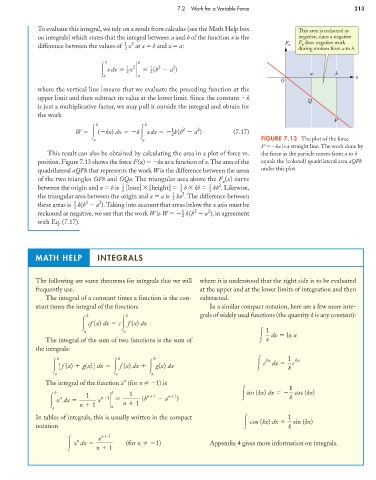
To evaluate this integral, we rely on a result from calculus (see the Math Help box This area is reckoned as
on integrals) which states that the integral between a and b of the function x is the negative, since a negative
2
1
x
difference between the values of x at x b and x a: F x F does negative work
2 during motion from a to b.
b x dx 1 2 b 1 2 (b a )
2
2
x `
2
a a a b x
O
where the vertical line ƒ means that we evaluate the preceding function at the
upper limit and then subtract its value at the lower limit. Since the constant k
Q
is just a multiplicative factor, we may pull it outside the integral and obtain for
the work
P
1 2 2
b
b
W ( kx) dx k x dx k (b a ) (7.17)
2
a a FIGURE 7.13 The plot of the force
F kx is a straight line. The work done by
This result can also be obtained by calculating the area in a plot of force vs. the force as the particle moves from a to b
position. Figure 7.13 shows the force F(x) kx as a function of x.The area of the equals the (colored) quadrilateral area aQPb
quadrilateral aQPb that represents the work W is the difference between the areas under this plot.
of the two triangles OPb and OQa. The triangular area above the F (x) curve
x
2
1
1
1
between the origin and x b is [base] [height] b kb kb . Likewise,
2
2
2
2
1
the triangular area between the origin and x a is ka . The difference between
2
2
2
1
these areas is k(b a ).Taking into account that areas below the x axis must be
2
2
2
1
reckoned as negative, we see that the work W is W k(b a ), in agreement
2
with Eq. (7.17).
MATH HELP INTEGRALS
The following are some theorems for integrals that we will where it is understood that the right side is to be evaluated
frequently use. at the upper and at the lower limits of integration and then
The integral of a constant times a function is the con- subtracted.
stant times the integral of the function: In a similar compact notation, here are a few more inte-
b cf (x) dx c b f (x) dx grals of widely used functions (the quantity k is any constant):
a a 1
x
The integral of the sum of two functions is the sum of dx ln x
the integrals:
b 3 f (x) g(x)4 dx b f (x) dx b g(x) dx e dx 1 k x
k x
e
k
a a a
n
The integral of the function x (for n Z 1) is 1
1
b x dx 1 x n 1 ` b n 1 (b n 1 a n 1 ) sin (kx) dx cos (kx)
k
n
a n 1 a
1
In tables of integrals, this is usually written in the compact cos (kx) dx sin (kx)
notation k
x dx x n 1 (for n
1) Appendix 4 gives more information on integrals.
n
n 1