Page 392 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 392
368 Cardiac MRI vs PET Scan
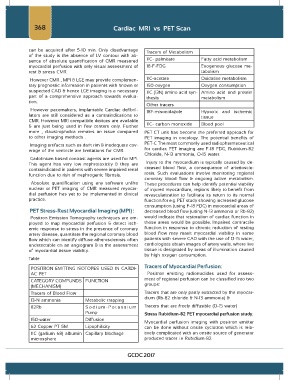
can be acquired after 5-10 min. Only disadvantage Tracers of Metabolism
of the study is the absence of LV contour with ab-
sence of absolute quantification of CMR measured 11C- palmitate Fatty acid metabolism
myocardial perfusion with only visual assessment of 18-F-FDG Exogenous glucose me-
rest & stress CMR. tabolism
However CMR , MPI & LGE may provide complemen- 11C-acetate Oxidative metabolism
tary prognostic information in patients with known or 150-oxygen Oxygen consumption
suspected CAD & hence LGE imaging is a necessary 11C (13N) amino acid syn- Amino acid and protein
part of a comprehensive approach towards evalua- thesis metabolism
tion.
Other tracers
However pacemakers, implantable Cardiac defibril- 18F-misonidazole Hypoxic and ischemic
lators are still considered as a contraindications to tissue
CMR. However MRI compatible devices are available
& are just being used in few centers only. Further 11C- carbon monoxide Blood pool
more , claustrophobia remains an issue compared PET CT unit has become the preferred approach for
to other imaging methods . PET imaging in oncology. The potential benefits of
Imaging artifacts such as dark rim & inadequate cov- PET-C The most commonly used radiopharmaceutical
erage of the ventricle are limitations for CMR. for cardiac PET imaging are F-18 FDG, Rubidum-82
Chloride, N-13 ammonia, O-15 water.
Gadolinium based contrast agents are used for MPI.
This agent has very low nephrotoxicity & they are Injury to the myocardium is typically caused by de-
contraindicated in patients with severe impaired renal creased blood flow, a consequence of arterioscle-
function due to risk of nephrogenic fibrosis. rosis. Such evaluations involve monitoring regional
coronary blood flow & ongoing active metabolism.
Absolute quantification using any software unlike These procedures can help identify potential viability
nuclear or PET imaging of CMR measured myocar- of injured myocardium, regions likely to benefit from
dial perfusion has yet to be implemented in clinical revascularization to facilitate its return to its normal
practice. function for e.g. PET study showing increased glucose
consumption (using F-18 FDG) in myocardial areas of
PET Stress-Rest Myocardial Imaging (MPI) : decreased blood flow (using N-13 ammonia or Rb-82)
Positron Emission Tomography techniques are em- would indicate that restoration of cardiac function in
ployed to map myocardial perfusion & detect isch- those areas would be possible. Impaired contractile
emic response to stress in the presence of coronary function in response to chronic reduction of resting
artery disease, quantitate the regional coronary blood blood flow may mask myocardial viability in some
flow which can identify diffuse atherosclerosis often patients with severe CAD with the use of O-15 water,
undetectable on an angiogram & in the assessment cardiologists obtain images of artery walls, where live
of myocardial tissue viability. tissue is designated by areas of illumination caused
by high oxygen consumption.
Table
POSITRON EMITTING ISOTOPES USED IN CARDI- Tracers of Myocardial Perfusion:
AC PET Positron emitting radionuclides used for assess-
ment of regional perfusion can be classified into two
CATEGORY COMPUNDS FUNCTION
(MECHANISM) groups:
Tracers of Blood Flow Tracers that are only partly extracted by the myocar-
dium (Rb-82 chloride & N-13 ammonia) &
13-N ammonia Metabolic trapping
82Rb Sodium-Potassium Tracers that are freely diffusible (O-15 water)
Pump Stress Rubidium-82 PET myocardial perfusion study.
150-water Diffusion
Myocardial perfusion imaging with positron emitter
62 Copper PT SM Lipophilicity can be done without onsite cyclotron which is rela-
11C (gallium 68) albumin Capillary blockage tively complicated with an onsite source of generator
microsphere produced tracer i.e Rubidium-82.
GCDC 2017