Page 394 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 394
370 Cardiac MRI vs PET Scan
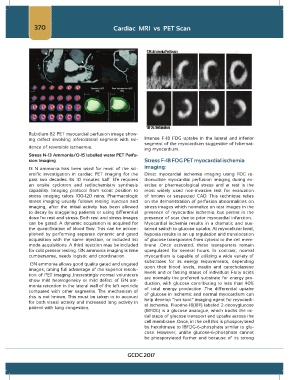
Rubidium-82 PET myocardial perfusion image show-
ing defect involving inferolateral segment with evi- Intense F-18 FDG uptake in the lateral and inferior
dence of reversible ischaemia. segment of the myocardium suggestive of hibernat-
ing myocardium.
Stress N-13 Ammonia/O-15 labelled water PET Perfu-
sion Imaging Stress F-18 FDG PET myocardial ischemia
13 N ammonia has been used for most of the sci- imaging:
entific investigation in cardiac PET imaging for the Direct myocardial ischemia imaging using FDG ra-
past two decades. Its 10 minutes half –life requires dionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging during ex-
an onsite cyclotron and radiochemistry synthesis ercise or pharmacological stress and at rest is the
capability. Imaging protocol from scout position to most widely used non-invasive test for evaluation
stress imaging takes 100-120 mins. Pharmacologic of known or suspected CAD. This technique relies
stress imaging usually follows resting injection and on the demonstration of perfusion abnormalities on
imaging, after the initial activity has been allowed stress images which normalize on rest images in the
to decay by staggering patients or using differential presence of myocardial ischemia, but persist in the
dose for rest and stress. Both rest and stress images presence of scar due to prior myocardial infarction.
can be gated. A dynamic acquisition is acquired for Myocardial ischemia results in a dramatic and sus-
the quantification of blood flow. This can be accom- tained switch to glucose uptake. At myocellular level,
plished by performing separate dynamic and gated hypoxia results in an up regulation and translocation
acquisition with the same injection, or included list of glucose transporters from cytosol to the cell mem-
mode acquisitions .A third injection may be included brane .Once activated, these transporters remain
for cold pressor testing. 13N ammonia imaging is time upregulated for several hours. In contrast, normal
cumbersome, needs logistic and coordination. myocardium is capable of utilizing a wide variety of
substrates for its energy requirements, depending
13N ammonia allows good quality gated and ungated upon their blood levels, insulin and catecholamine
images, taking full advantage of the superior resolu- levels and or fasting status of individual. Fatty acids
tion of PET imaging .Interestingly normal volunteers are normally the preferred substrate for energy pro-
show mild heterogeneity or mild defect of 13N am- duction, with glucose contributing to less than 40%
monia retention in the lateral wall of the left ventricle of total energy production .The differential uptake
compared with other segments. The mechanism of of glucose in ischemic and normal myocardium can
this is not known. This must be taken in to account help develop “hot spot” imaging agent for myocardi-
for both visual activity and increased lung activity in al ischemia. Fluorine-18(18F) labeled 2-deoxyglucose
patient with lung congestion.
(18FDG) is a glucose analogue, which tracks the ini-
tial steps of glucose transport and uptake across the
cell membrane .Once, in the cell this is phosporylated
by hexokinase to 18FDG-6-phosphate similar to glu-
cose. However, unlike glucose-6-phosphate cannot
be phosporylated further and because of its strong
GCDC 2017