Page 423 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 423
408 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
NURSING ALERT
A drop in hemoglobin below 10 g/dL or a trend downward from baseline should be
reported to the physician. A sudden drop can indicate bleeding, and a gradual drop
can point to anemia.
NURSING ALERT
A decrease in platelets below 30,000 warns the nurse that bleeding, especially intrac-
ranial, can occur. Institute bleeding precautions and notify the physician ASAP!
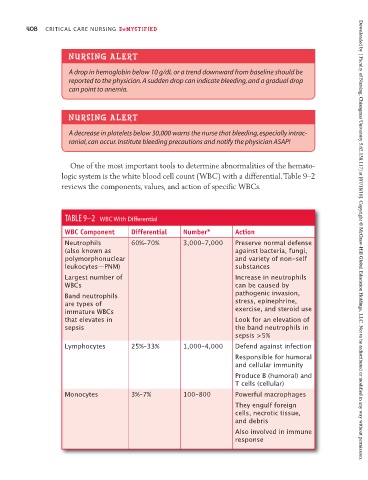
One of the most important tools to determine abnormalities of the hemato-
logic system is the white blood cell count (WBC) with a differential. Table 9–2
reviews the components, values, and action of specific WBCs.
TABLE 9–2 WBC With Differential
WBC Component Differential Number * Action
Neutrophils 60%–70% 3,000–7,000 Preserve normal defense Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
(also known as against bacteria, fungi,
polymorphonuclear and variety of non-self
leukocytes—PNM) substances
Largest number of Increase in neutrophils
WBCs can be caused by
Band neutrophils pathogenic invasion,
are types of stress, epinephrine,
immature WBCs exercise, and steroid use
that elevates in Look for an elevation of
sepsis the band neutrophils in
sepsis >5%
Lymphocytes 25%–33% 1,000–4,000 Defend against infection
Responsible for humoral
and cellular immunity
Produce B (humoral) and
T cells (cellular)
Monocytes 3%–7% 100–800 Powerful macrophages
They engulf foreign
cells, necrotic tissue,
and debris
Also involved in immune
response