Page 425 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 425
410 CRITICAL CARE NURSING DeMYSTIFIED
NURSING ALERT
The nurse should assess the number of band neutrophils in any patient suspected of
having an infection. An increase greater than 5% is called a shift-to-the-left, indicat-
ing the proliferation of immature granulocytes in response to bacterial infection.
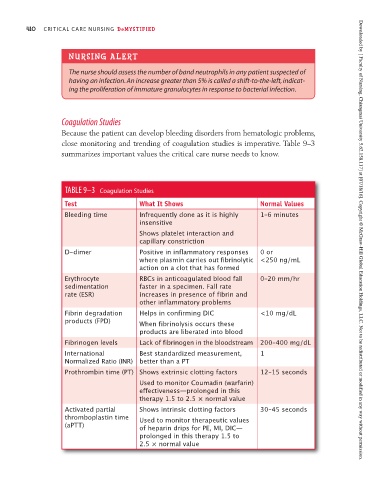
Coagulation Studies
Because the patient can develop bleeding disorders from hematologic problems,
close monitoring and trending of coagulation studies is imperative. Table 9–3
summarizes important values the critical care nurse needs to know.
TABLE 9–3 Coagulation Studies
Test What It Shows Normal Values
Bleeding time Infrequently done as it is highly 1–6 minutes
insensitive
Shows platelet interaction and
capillary constriction Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
D-dimer Positive in inflammatory responses 0 or
where plasmin carries out fibrinolytic < 250 ng/mL
action on a clot that has formed
Erythrocyte RBCs in anticoagulated blood fall 0–20 mm/hr
sedimentation faster in a specimen. Fall rate
rate (ESR) increases in presence of fibrin and
other inflammatory problems
Fibrin degradation Helps in confirming DIC <10 mg/dL
products (FPD) When fibrinolysis occurs these
products are liberated into blood
Fibrinogen levels Lack of fibrinogen in the bloodstream 200–400 mg/dL
International Best standardized measurement, 1
Normalized Ratio (INR) better than a PT
Prothrombin time (PT) Shows extrinsic clotting factors 12–15 seconds
Used to monitor Coumadin (warfarin)
effectiveness—prolonged in this
therapy 1.5 to 2.5 × normal value
Activated partial Shows intrinsic clotting factors 30–45 seconds
thromboplastin time Used to monitor therapeutic values
(aPTT) of heparin drips for PE, MI, DIC—
prolonged in this therapy 1.5 to
2.5 × normal value