Page 424 - Critical Care Nursing Demystified
P. 424
Chapter 9 CARE OF THE PATIENT WITH CRITICAL HEMATOLOGIC NEEDS 409
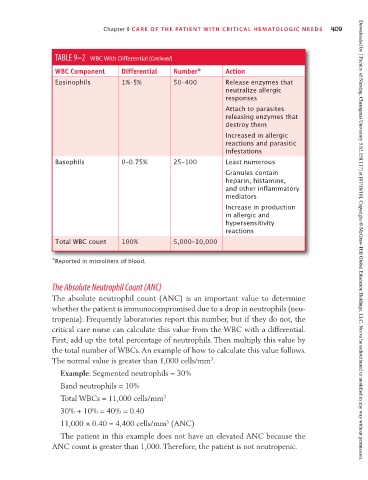
TABLE 9–2 WBC With Differential (Continued)
WBC Component Differential Number * Action
Eosinophils 1%–5% 50–400 Release enzymes that
neutralize allergic
responses
Attach to parasites
releasing enzymes that
destroy them
Increased in allergic
reactions and parasitic
infestations
Basophils 0–0.75% 25–100 Least numerous
Granules contain
heparin, histamine,
and other inflammatory
mediators
Increase in production
in allergic and
hypersensitivity
reactions
Total WBC count 100% 5,000–10,000 Downloaded by [ Faculty of Nursing, Chiangmai University 5.62.158.117] at [07/18/16]. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Global Education Holdings, LLC. Not to be redistributed or modified in any way without permission.
∗ Reported in microliters of blood.
The Absolute Neutrophil Count (ANC)
The absolute neutrophil count (ANC) is an important value to determine
whether the patient is immunocompromised due to a drop in neutrophils (neu-
tropenia). Frequently laboratories report this number, but if they do not, the
critical care nurse can calculate this value from the WBC with a differential.
First, add up the total percentage of neutrophils. Then multiply this value by
the total number of WBCs. An example of how to calculate this value follows.
The normal value is greater than 1,000 cells/mm .
3
Example: Segmented neutrophils = 30%
Band neutrophils = 10%
Total WBCs = 11,000 cells/mm 3
30% + 10% = 40% = 0.40
11,000 × 0.40 = 4,400 cells/mm (ANC)
3
The patient in this example does not have an elevated ANC because the
ANC count is greater than 1,000. Therefore, the patient is not neutropenic.