Page 653 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 653
472 PART 4: Pulmonary Disorders
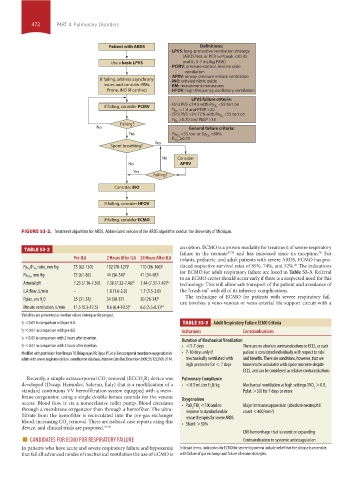
Patient with ARDS Definitions:
- LPVS: lung-protective ventilation strategy
(ARDS Net, or PCV w/Ppeak <30-35
Use a basic LPVS and V T 5-7 mL/kg PBW)
- PCIRV: pressure control, inverse ratio
ventilation
- APRV: airway pressure release ventilation
If failing, address asynchrony - iNO: inhaled nitric oxide
issues and consider: RMs, - RM: recruitment maneuvers
Prone, iNO (if cardiac) - HFOV: high-frequency oscillatory ventilation
LPVS failure criteria:
If failing, consider PCIRV - On LPVS <24 h with Pa O 2 <55 torr on
= 1.0 and PEEP >20
Fi O 2
<55 torr on
- On LPVS >24-72 h with Pa O 2
>0.70 and PEEP >15
Fi O 2
Failing?
No General failure criteria:
Yes <88%
- Pa O 2 <55 torr or Sp O 2
≥0.70
- Fi O 2
Yes
Spont breathing?
No Consider
No APRV
Yes
Failing?
Consider iNO
If failing, consider HFOV
If failing, consider ECMO
FIGURE 53-2. Treatment algorithm for ARDS. Abbreviated version of the ARDS algorithm used at the University of Michigan.
an option. ECMO is a proven modality for treatment of severe respiratory
TABLE 53-2
failure in the neonate 37,38 and has increased since its inception. For
39
Pre-ILA 2 Hours After ILA 24 Hours After ILA infants, pediatric, and adult patients with severe ARDS, ECMO has pro-
40
ratio, mm Hg 75 (62-130) 102 (70-127) a 110 (86-160) a duced respective survival rates of 85%, 74%, and 52%. The indications
Pa O 2 /Fi O 2
for ECMO for adult respiratory failure are listed in Table 53-3. Referral
, mm Hg 73 (61-86) 44 (36-54) b 41 (34-48) b
to an ECMO center should occur early if there is a suspected need for this
Pa CO 2
Arterial pH 7.23 (7.16-7.30) 7.38 (7.32-7.46) b 7.44 (7.37-7.49) b,c technology. This will allow safe transport of the patient and avoidance of
iLA flow, L/min – 1.8 (1.6-2.0) 1.7 (1.5-2.0) the “crash on” with all of its inherent complications.
The technique of ECMO for patients with severe respiratory fail-
Pplat, cm H O 35 (31-38) 34 (30-37) 30 (26-34) b
2 ure involves a veno-venous or veno-arterial life support circuit with a
Minute ventilation, L/min 11.5 (9.3-12.5) 8.6 (6.4-10.5) b 6.6 (5.5-8.3) b,d
Variables are presented as median values (interquartile ranges).
a p <0.05 in comparison with pre-iLA. TABLE 53-3 Adult Respiratory Failure ECMO Criteria
b p <0.01 in comparison with pre-iLA. Indications Contraindications
c p <0.05 in comparison with 2 hours after insertion. Duration of Mechanical Ventilation
d p <0.01 in comparison with 2 hours after insertion. • <5-7 days There are no absolute contraindications to ECLS, as each
Modified with permission from Brogan TV, Thiagarajan RR, Rycus PT, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in • 7-10 days only if patient is considered individually with respect to risks
adults with severe respiratory failure: a multicenter database. Intensive Care Med. December 2009;35(12):2105-2114. mechanically ventilated with and benefits. There are conditions, however, that are
high pressures for < 7 days known to be associated with a poor outcome despite
ECLS, and can be considered as relative contraindications
Recently, a simple extracorporeal CO removal (ECCO R) device was Pulmonary Compliance
2
2
developed (Decap, Hemodec, Salerno, Italy) that is a modification of a • <0.5 mL/cm H O/kg Mechanical ventilation at high settings (FiO >0.9,
standard continuous VV hemofiltration system equipped with a mem- 2 Pplat >30) for 7 days or more 2
brane oxygenator, using a single double-lumen cannula for the venous Oxygenation
access. Blood flow is via a nonocclusive roller pump. Blood circulates • PaO /FiO <100 and no Major immunosuppression (absolute neutrophil
2
2
through a membrane oxygenator then through a hemofilter. The ultra- response to standard and/or count <400/mm ) 3
filtrate from the hemofilter is recirculated into the pre-gas exchanger rescue therapies for severe ARDS
blood, increasing CO removal. There are isolated case reports using this • Shunt >30%
2
device, and clinical trials are proposed. 34-36 CNS hemorrhage that is recent or expanding
■ CANDIDATES FOR ECMO FOR RESPIRATORY FAILURE Contraindication to systemic anticoagulation
In patients who have acute and severe respiratory failure and hypoxemia In broad terms, indications for ECMO for severe hypoxemia include belief that the disease is reversible,
that fail all advanced modes of mechanical ventilation the use of ECMO is with failure of gas exchange and failure of rescue strategies.
section04.indd 472 1/23/2015 2:19:51 PM