Page 655 - Hall et al (2015) Principles of Critical Care-McGraw-Hill
P. 655
474 PART 4: Pulmonary Disorders
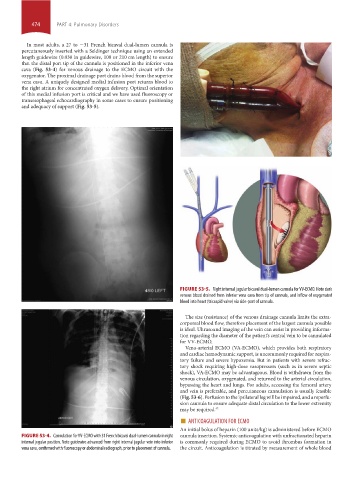
In most adults, a 27 to −31 French bicaval dual-lumen cannula is
percutaneously inserted with a Seldinger technique using an extended
length guidewire (0.038 in guidewire, 100 or 210 cm length) to ensure
that the distal port tip of the cannula is positioned in the inferior vena
cava (Fig. 53-4) for venous drainage to the ECMO circuit with the
oxygenator. The proximal drainage port drains blood from the superior
vena cava. A uniquely designed medial infusion port returns blood to
the right atrium for concentrated oxygen delivery. Optimal orientation
of this medial infusion port is critical and we have used fluoroscopy or
transesophageal echocardiography in some cases to ensure positioning
and adequacy of support (Fig. 53-5).
FIGURE 53-5. Right internal jugular bicaval dual-lumen cannula for VV-ECMO. Note dark
venous blood drained from inferior vena cava from tip of cannula, and inflow of oxygenated
blood into heart (tricuspid valve) via side-port of cannula.
The size (resistance) of the venous drainage cannula limits the extra-
corporeal blood flow, therefore placement of the largest cannula possible
is ideal. Ultrasound imaging of the vein can assist in providing informa-
tion regarding the diameter of the patient’s central vein to be cannulated
for VV-ECMO.
Veno-arterial ECMO (VA-ECMO), which provides both respiratory
and cardiac hemodynamic support, is uncommonly required for respira-
tory failure and severe hypoxemia. But in patients with severe refrac-
tory shock requiring high-dose vasopressors (such as in severe septic
shock), VA-ECMO may be advantageous. Blood is withdrawn from the
venous circulation, oxygenated, and returned to the arterial circulation,
bypassing the heart and lungs. For adults, accessing the femoral artery
and vein is preferable, and percutaneous cannulation is usually feasible
(Fig. 53-6). Perfusion to the ipsilateral leg will be impaired, and a reperfu-
sion cannula to ensure adequate distal circulation to the lower extremity
may be required. 42
■ ANTICOAGULATION FOR ECMO
An initial bolus of heparin (100 units/kg) is administered before ECMO
FIGURE 53-4. Cannulation for VV-ECMO with 31 French bicaval dual-lumen cannula in right cannula insertion. Systemic anticoagulation with unfractionated heparin
internal jugular position. Note guidewire advanced from right internal jugular vein into inferior is commonly required during ECMO to avoid thrombus formation in
vena cava, confirmed with fluoroscopy or abdominal radiograph, prior to placement of cannula. the circuit. Anticoagulation is titrated by measurement of whole blood
section04.indd 474 1/23/2015 2:19:56 PM